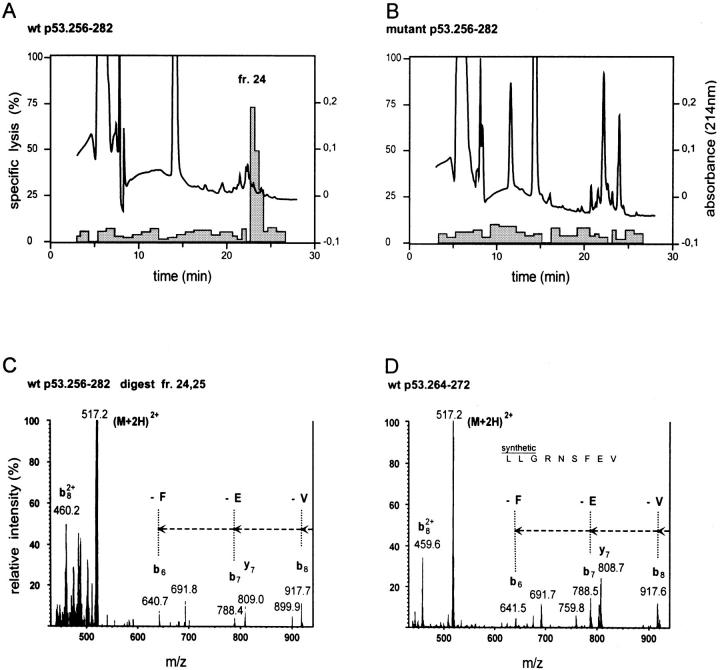
Figure 6.
The p53.264–272 CTL epitope is generated by proteasomal degradation of the WT as opposed to the mutant 27-mer p53.256–282 polypeptide substrate. Bulk 20S proteasome– degraded (24-h) WT and mutant 27-mer peptide products were fractionated by RP-HPLC. 51Cr-labeled T2 target cells were pulsed for 40 min under serum-free conditions with half of each of the WT and mutant HPLC fractions and tested for susceptibility to lysis by CTL A2 264 at an E/T ratio of 20:1 in a 6-h 51Cr-release assay. The HPLC profile (absorbance: —) and the specific lysis (shaded columns) of T2 targets sensitized with individual WT (A) and mutant (B) HPLC fractions is shown. WT fractions 24 and 25 were pooled and tested by MS/MS for detection of the p53.264–272 (LLGRNSFEV) peptide epitope. Ions of m/z = 517.2 corresponding to the double protonated 264–272 9-mer peptide were fragmented by argon atoms. Collision-activated dissociation fragments of m/z 517.2 and derived from the pooled WT fractions 24 and 25 (C) were compared with those obtained after argon atom–mediated fragmentation of the synthetic 264–272 peptide (D). In particular, fragments b8, b7, and b6, lacking the COOH-terminal residues V, E, and F, respectively, were detectable in both the pooled WT fractions 24 and 25 (C) and the synthetic 264–272 9-mer peptide (D).