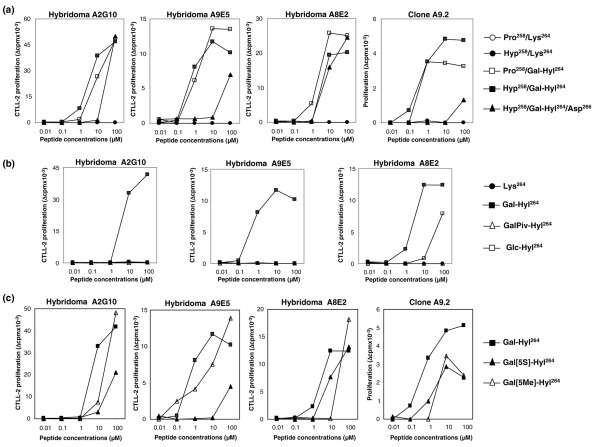
Figure 2.
T-cell reactivities of hybridomas A2G10, A9E5 and A8E2, and clone A9.2 to several CII256–270 analogues. T cells were stimulated with increasing concentrations of synthetic peptides in the presence of antigen-presenting cells, and their responses were assessed by quantification of interleukin-2 secretion in the supernatant or measurement of proliferation for the hybridomas and the T-cell clone, respectively. Data are expressed as means of two to five individual experiments. (a) Recognition of a panel of naturally occurring peptides synthesized with or without the potential post-translational modifications at positions 258 and/or 264. The murine peptide comprises a Glu266→Asp substitution. (b) Loss of hybridoma reactivity following changes targeting the galactose molecule linked to Hyl264. (c) Comparison of T-cell hybridoma and clone reactivities to cognate glycopeptide and derivatives modified at sugar anchor position. CII256–270, immunodominant epitope of bovine type II collagen.