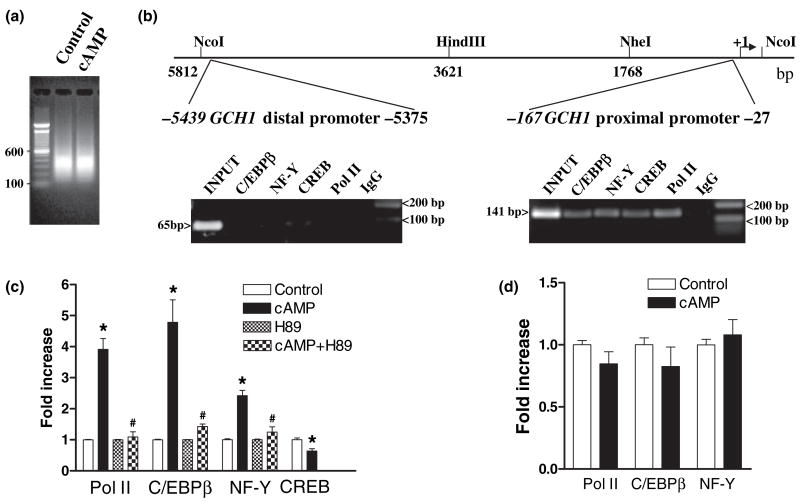
Fig. 3.
Protein kinase A-dependent recruitment of PolII, C/EBPβ and NF-Y but not CREB to the GCH1 proximal promoter. (a) Sonication of cross-linked DNA from control and 8Br-cAMP-treated PC12 cells reproducibly generates average size fragments of 400 bp. (b) A schematic of the rat GCH1 5′ flanking region showing the locations of proximal and distal promoter regions amplified by PCR relative to the transcription start site ( + 1). Electrophoresis of PC12 ChIP PCR reactions using GCH1 proximal and distal promoter primer pairs identified amplicons of the correct size and shows that under basal conditions Pol II, CREB, C/EBPβ and NF-Y are associated with the proximal but not distal promoter. (c) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of PC12 ChIP samples using GCH1 proximal promoter primers shows that Pol II, C/EBPβ and NF-Y but not CREB are recruited to the proximal promoter in response to 1 h incubation with 5 mmol/L 8Br-cAMP (cAMP) and that recruitment is blocked by the PKA inhibitor H89 (cAMP + H89) which has no effect on its own (H89). (d) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of 126-1B2 cell ChIP samples using GCH1 proximal promoter primers shows that Pol II, C/EBPβ and NF-Y are not recruited to the proximal promoter in response to 1 h incubation with 5 mmol/L 8Br-cAMP (cAMP). *p ≤ 0.05 when compared with respective control activity. #p ≤ 0.05 when compared with cAMP.