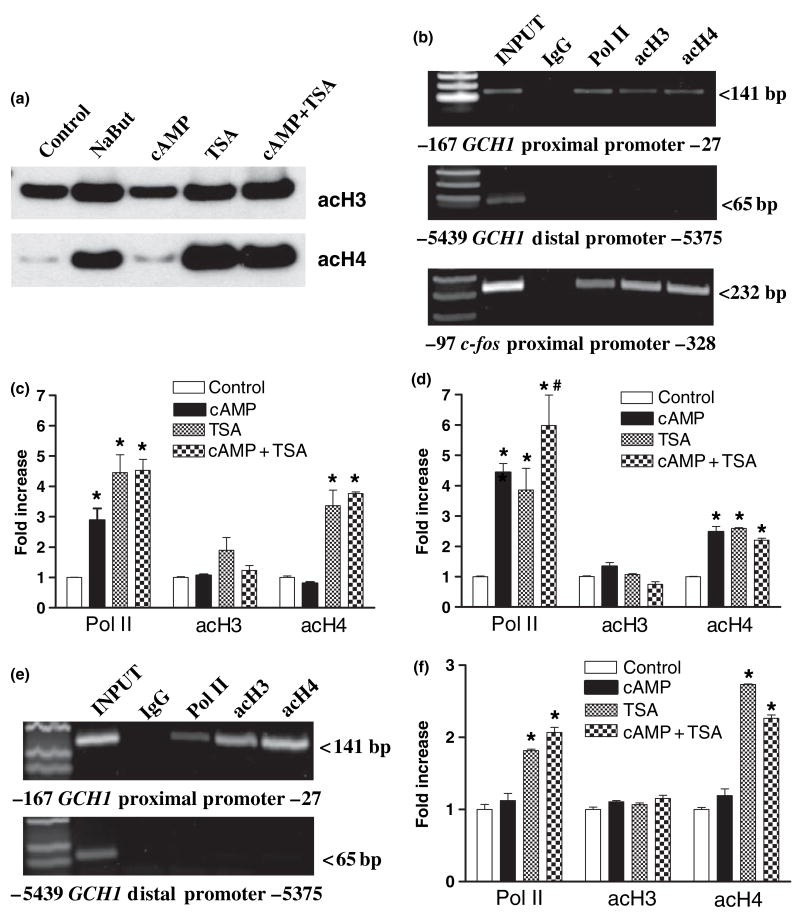
Fig. 4.
Recruitment of Pol II, C/EBPβ and NF-Y does not involve acetylation of histones H3 and H4 at GCH1 proximal promoter poised nucleosomes. (a) Western blots of equal amounts of acid-soluble proteins from PC12 cells treated for 1 h with 10 mmol/L sodium butyrate (NaBut), 5 mmol/L 8Br-cAMP (cAMP), 100 ng/mL of trichostatin A (TSA) or cAMP + TSA and probed with antibodies directed against K9,14 di-acetylated H3 (acH3) or K5,8,12,16 tetra-acetylated H4 (acH4). (b) Electrophoresis of PC12 ChIP PCR reactions using GCH1 proximal and distal promoter primer pairs shows that under basal conditions Pol II, acH3 and acH4 are associated with the proximal but not distal promoter. Similar analysis using c-fos proximal promoter primers identifies amplicons of the correct size associated with Pol II, acH3 and acH4 ChIP samples. (c) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of PC12 ChIP samples using GCH1 proximal promoter primers. Pol II is equally recruited in response to cAMP, TSA and cAMP + TSA. None of the treatments alter levels of acH3. In contrast, TSA and cAMP + TSA equally elevate acH4 levels. (d) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of PC12 ChIP samples using c-fos proximal promoter primers. Pol II is recruited in response to cAMP and TSA but Pol II recruitment following cAMP + TSA is greater than either treatment alone. None of the treatments alter levels of acH3. In contrast, cAMP, TSA and cAMP + TSA equally elevate levels of acH4. (e) Electrophoresis of C6 ChIP PCR reactions using GCH1 proximal and distal promoter primer pairs shows that under basal conditions Pol II, acH3 and acH4 are associated with the proximal but not distal promoter. (f) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of C6 ChIP samples using GCH1 proximal promoter primers. Pol II was not recruited in response to cAMP but was recruited following TSA and cAMP + TSA. None of the treatments alter levels of acH3. In contrast, TSA and cAMP + TSA both elevate acH4 levels. *p ≤ 0.05 when compared with respective control activity. #p ≤ 0.05 when compared with cAMP or TSA alone.