Fig. 3.
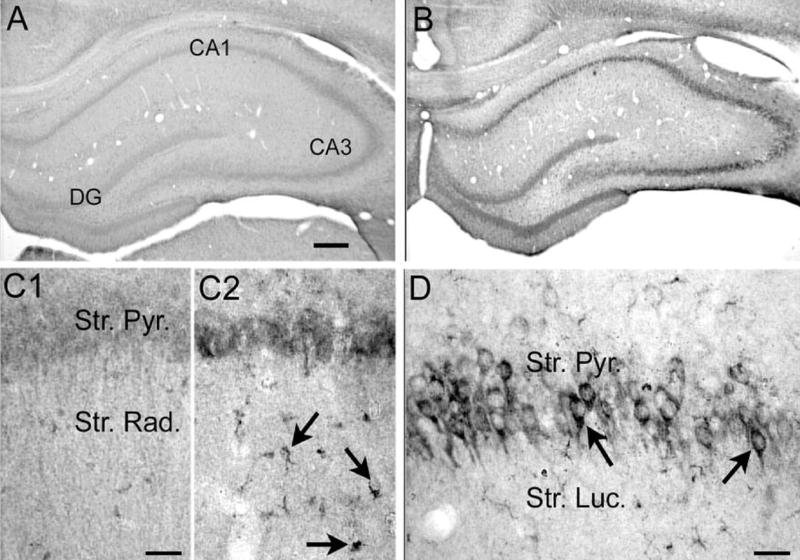
Increased VEGF protein expression in hippocampus 24 h after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. (A, B) Sections from an (A) saline- and (B) pilocarpine-treated rat that had 60 min of status epilepticus were processed together using an antibody to VEGF (see Experimental Procedures). Increased VEGF protein was evident in the cell layers. DG=dentate gyrus. Scale bar=200 μm. (C) Increased magnification of area CA1 from (C1) and (C2) shows that glial-like structures were associated with increased VEGF immunoreactivity after pilocarpine-induced status compared with controls. Scale bar=50 μm. (D) A different section from a pilocarpine-treated rat that had status epilepticus, showing increased VEGF immunore-activity in area CA3 pyramidal cell somata. Scale bar=100 μm.
