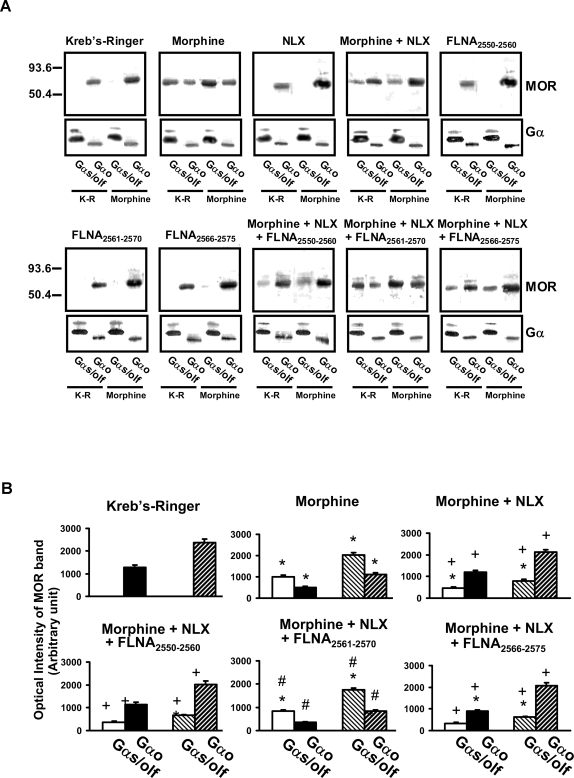
Figure 7. FLNA2561-2565 blocks 10 pM NLX's prevention of the chronic morphine-induced Go-to-Gs coupling switch.
Striatal slices were chronically treated with vehicle, morphine, NLX, morphine+NLX, or with one of the three FLNA peptides alone or in combination with morphine+NLX. Coupling between MOR and Gs/Go proteins was assessed by Western blot (A) and analyzed by densitometric scanning (B). Chronic morphine exposure caused a Go-to-Gs coupling switch that was blocked by NLX co-treatment. NLX's suppression of this coupling switch was blocked by FLNA2561-2570 but not by FLNA2566–2575 or FLNA2550–2560, illustrating that NLX's protective effect occurs via its binding to FLNA within FLNA2561–2570. Solid bars indicate basal coupling; hatched bars indicate coupling after in vitro morphine stimulation. n = 6. *p<0.01 compared to Kreb's Ringer; +p<0.01 compared to morphine; #p<0.01 compared to morphine+NLX.