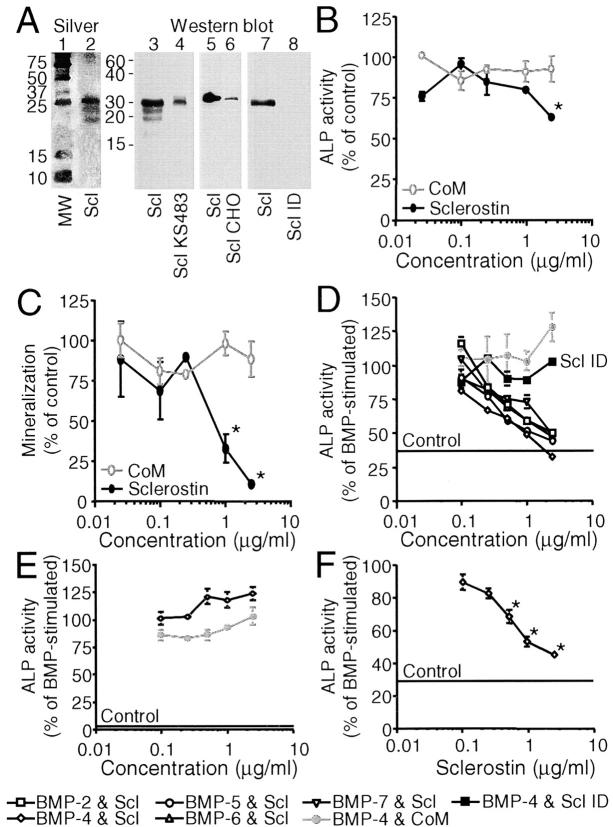
Figure 5.
Sclerostin inhibits unstimulated and BMP-stimulated osteoblastic differentiation of KS483 and primary human MSCs, but not of C2C12 cells. Silver staining (lanes 1 and 2) and Western blotting with a rabbit anti–human sclerostin antibody (lanes 3–8) of human sclerostin (lanes 2 [100 ng/ml], 3 [500 ng/ml], 5 [100 ng/ml], and 7 [100 ng/ml]), sclerostin containing medium of KS483 (lane 4), CHO cells (lane 6), and immunodepleted sclerostin preparation (lane 8, equal volume as 100 ng/ml sclerostin preparation) run under reducing conditions (A). Long-term (18 d) osteogenic KS483 cell cultures were treated with sclerostin (2.5 μg/ml or concentrations indicated) or CoM (equal volume) from day 4 onwards and analyzed for ALP activity (B) and mineralization (C). Confluent KS483 were stimulated with BMPs (50 ng/ml BMP-2, 50 ng/ml BMP-4, 300 ng/ml BMP-5, 100 ng/ml BMP-6, and 300 ng/ml BMP-7) in the absence or presence of the dose range of sclerostin or CoM. ALP activity was measured kinetically 4 d after stimulation (D). Confluent C2C12 cells were stimulated with 50 ng/ml BMP-4 in the absence or presence of the dose range of sclerostin or CoM. ALP activity was measured kinetically 4 d after stimulation (E). Confluent hMSCs were stimulated with 100 ng/ml BMP-4 in the absence or presence of the dose range of sclerostin. ALP activity was measured kinetically 4 d after stimulation (F). CoM, Control medium. hMSCs, human mesenchymal stromal cells. MW, molecular weight marker. Scl, sclerostin. Scl CHO, sclerostin containing medium of CHO cells. Scl ID, Immunodepleted sclerostin preparation. Scl KS483, sclerostin containing medium of KS483 cells. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of triplicate (B and C) or octagonal (D–F) experiments relative to control (B and C) and BMP stimulation (D–F) that was set at 100%. *, Significant versus CoM (P < 0.05). Statistical differences were omitted from C for clarity.