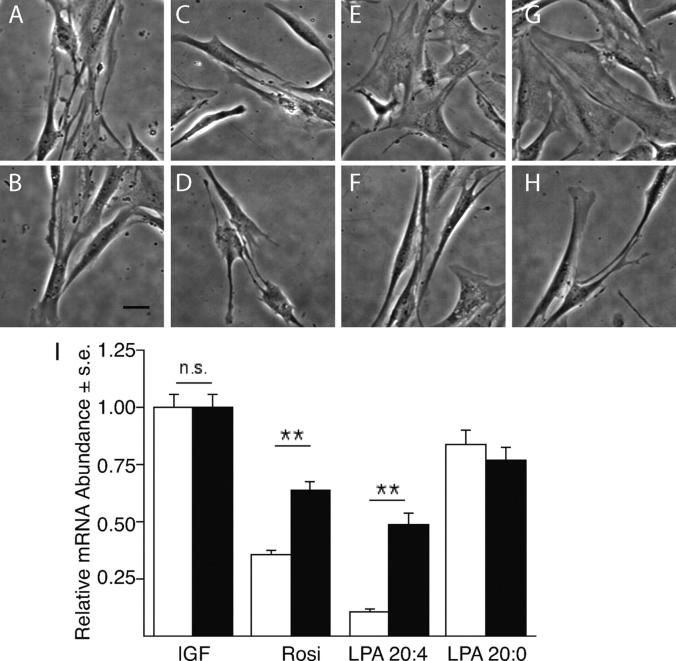
Figure 8.
PPARγ agonists elicit phenotypic modulation and dedifferentiation of VSMCs in vitro. VSMC cultures established in the presence of 2 ng/ml IGF-1 (A) were treated with 1 μM of each LPA 20:0 (C), LPA 20:4 (E), and Rosi (G) for 3 d. LPA 20:4 and Rosi treatments lead to a pronounced change in the morphology of VSMCs. Pretreatment of the cultures with 200 nM GW9662 for 30 min did not affect the spindle-like morphology of the IGF-1– (B) and LPA 20:0-treated cultures (D). In contrast, GW9662 reversed the flattened morphology into a spindle-like shape in cultures treated with LPA 20:4 (F) and Rosi (H, calibration bar 100 μm). Expression of hCAD mRNA decreased significantly by day 5 in VSMCs treated with Rosi and LPA (I, white bars) compared with the IGF-treated control cultures. This trend was reversed in cultures pretreated with 200 nM GW9662 (I, black bars) as the PPARγ antagonist caused a significant increase in the abundance of hCAD mRNA measured by quantitative RT-PCR (P < 0.01, ANOVA).