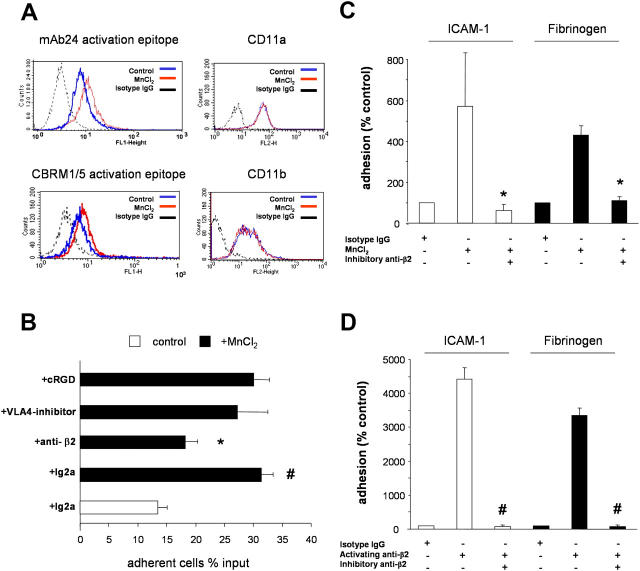
Figure 2.
Integrins and EPC adhesion. (A) EPCs were activated with 2 mM MnCl2 for 30 min. Activation of integrins was determined by CBRM1/5 and mAb24 antibodies (left) and expression of CD11a and CD11b was controlled by FACS analysis (right; n = 3). (B) Adhesion of EPCs to 10 ng/ml TNF-α–prestimulated HUVECs was stimulated where indicated with MnCl2. 105 EPCs/well (in 100 μl adhesion buffer) were added to the HUVEC monolayers in the absence or presence of 30 μg/ml of blocking monoclonal anti–β2-integrin antibodies (clone IB4 or mAb 60.3), 30 μg/ml of murine isotype control antibodies, 50 μM of the inhibitory agents cyclic RGD peptide or 50 μM of VLA-4-inhibitor. The total number of EPCs added to the well is set as 100%. *, P < 0.01 versus MnCl2 + isotype antibody; #, P < 0.01 versus isotype control. (C and D) EPCs were treated with 2 mM MnCl2 or 10 μg/ml β2-integrin–activating antibody. Adhesion to fibrinogen- or ICAM-1–coated plates was detected after 20 min in the presence or absence of β2-integrin–inhibitory antibody or isotype control antibodies (n = 4). *, P < 0.05 versus MnCl2 + isotype IgG; #, P < 0.05 versus activating anti-β2 + isotype IgG.