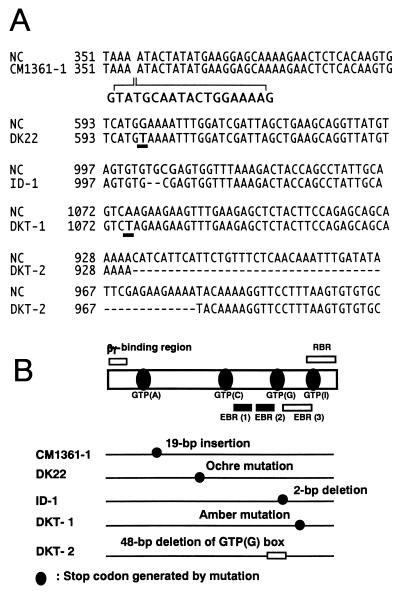
Figure 5.
Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of the cDNA of the α subunit (RGA1) of the recurrent parents with those from five alleles of Daikoku dwarf (d-1). (A) Sequences of the mutated regions of Daikoku dwarf (d-1), CM1361–1, DK22, DKT-1, ID-1 and DKT-2 are aligned. The numbers of nucleotides correspond to those in RGA1 of Nipponbare. The RGA1 sequences of the all recurrent cultivars (Nipponbare, Shiokari, Kinmaze, and Taichung 65) were identical and these recurrent cultivars were indicated as NC (normal cultivar). (B) Schematic diagram of the structure of the α subunit of rice heterotrimeric G protein and the positions of mutations in five alleles of Daikoku dwarf (d-1). Highly conserved regions among the α subunits from various plants and animals, four GTP-binding sites (A, C, G, and I) and two of three effector-binding regions (EBR1 and 2), are indicated by closed boxes and bars, respectively. The regions, which show low homology among the plant and animal subunits, a βγ-binding region, one of three effector-binding regions (EBR 3) and a receptor-binding region (RBR), are indicated by open bars. The positions of stop codons generated by mutations in the cDNAs from four alleles of Daikoku dwarf (d-1), CM1361–1, DK22, ID-1, and DKT-1, are indicated by closed circles. A GTP-binding site (G), which is deleted in the cDNA of DKT-2, is indicated as an open box.