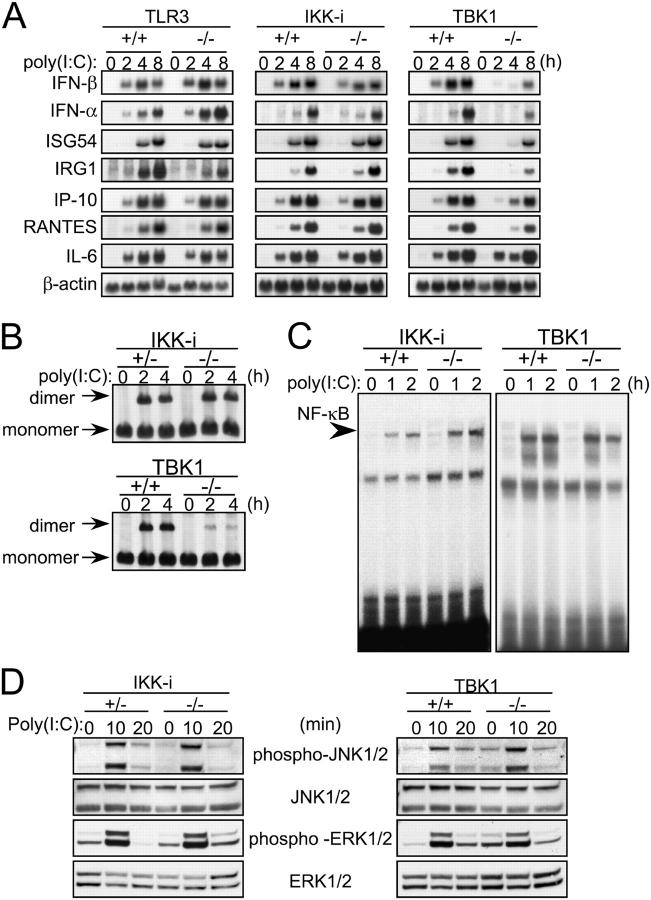
Figure 4.
Impaired induction of IFN-β and IFN-inducible genes in poly(I:C)-stimulated TBK1−/−, but not IKK-i −/− EFs. (A) mRNA induction in poly(I:C)-stimulated EFs. Wild-type, TLR3−/−, IKK-i −/−, or TBK1−/− EFs were transfected with 10 μg/ml poly(I:C) for the indicated period. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to Northern blot analysis for the indicated genes. (B) Formation of IRF-3 dimer upon poly(I:C) stimulation. Control (IKK-i +/− or TBK1+/+), IKK-i −/−, or TBK1−/− EFs were transfected with 10 μg/ml poly(I:C) and incubated for the indicated periods. Whole cell extracts were prepared and subjected to native PAGE. Monomeric and dimeric IRF-3 were detected by Western blotting. (C) NF-κB DNA binding activity. Wild-type, IKK-i −/−, or TBK1−/− EFs were stimulated with 10 μg/ml poly(I:C) for the times indicated, and NF-κB binding was determined by EMSA. (D) MAP kinase activation in poly(I:C)-stimulated EFs. Control (IKK-i +/− or TBK1+/+), IKK-i −/−, or TBK1−/− EFs were stimulated with 10 μg/ml poly(I:C) for the indicated periods. Whole cell lysates were prepared and blotted with antiphospho-JNK1/2 (phospho-JNK1/2) or antiphospho-ERK1/2 Ab (phospho-ERK1/2). The total amounts of JNK1/2 and ERK1/2 were also determined. One representative experiment from two independent experiments is shown.