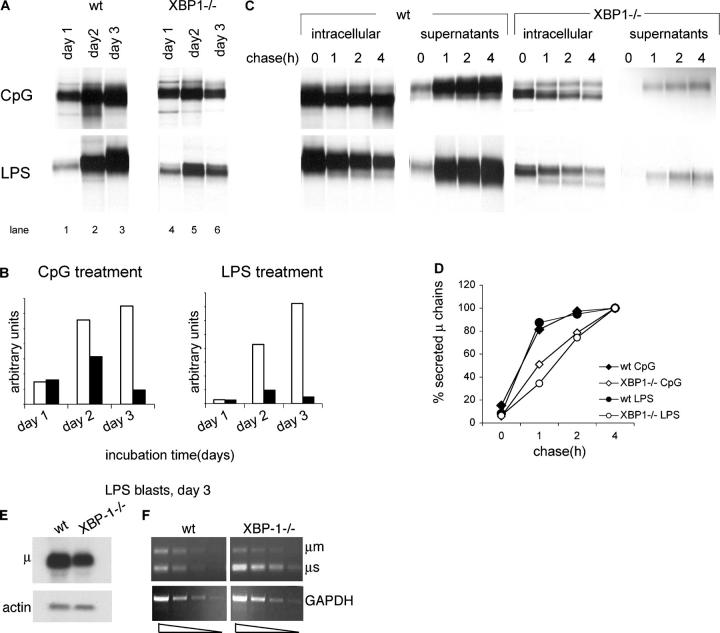
Figure 2.
High levels of biosynthesis and secretion of IgM require XBP-1. (A) 106 live cells, as determined by trypan blue exclusion, were pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine for 30 min. Cells were lysed in 1% SDS, and lysate was diluted to 0.07% SDS with NP-40 lysis mix followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-μ antibodies and analysis by SDS-PAGE (10%). (B) Autoradiograms were quantified by phosphoimager. Empty bars, WT B cells; black bars, XBP1−/− B cells. (C) Cells stimulated for 3 d with LPS or CpG were pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine for 30 min and chased for up to 4 h. Cells were lysed in 1% SDS; lysate was diluted to 0.07% SDS with NP-40 lysis mix followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-μ antibodies. At each time point, IgM also was recovered from the media by immunoprecipitated with anti-μ antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (10%). Each lane represents material from 106 live cells. (D) Autoradiograms were quantified by phosphoimager. Secreted μ chains were expressed as percentage from μ chains recovered after 4-h chase. (E) RNA was extracted from day 3 LPS-treated WT or XBP-1−/− B cells and analyzed by Northern blotting. Quantification indicates a 2.6-fold reduction in μ mRNA levels in XBP-1−/− cells. (F) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of cDNA prepared from RNA of day 3 LPS-treated WT or XBP-1−/− B cells. Threefold dilution series of the cDNA were used as input material for the PCR with primers specific for μ chains or GAPDH as a reference. The analysis indicates a less than threefold reduction in μ mRNA levels in XBP-1−/− cells.