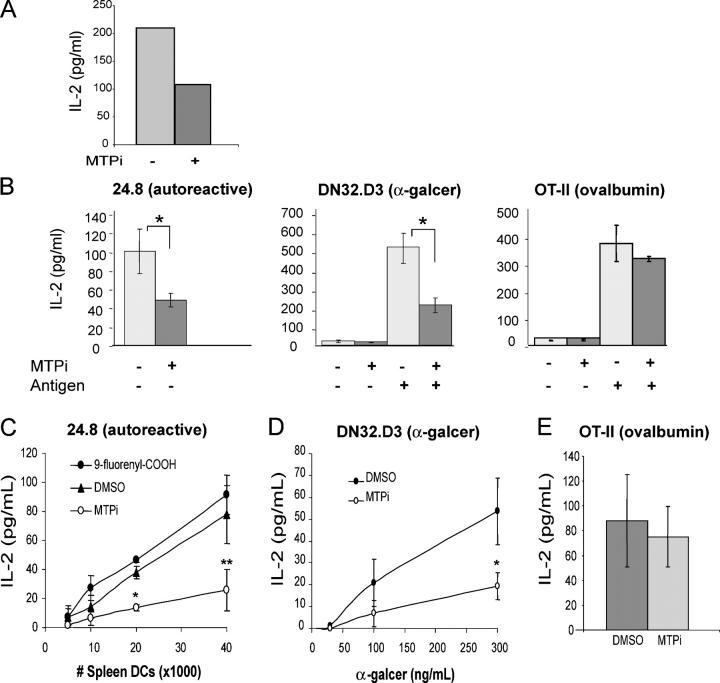
Figure 3.
Chemical inhibition of mouse MTP causes a selective defect in CD1d antigen presentation. (A) MODE-K cells cultured in the presence of BMS212122 (MTPi) or vehicle were incubated with α-galcer for 3 h, washed, and co-cultured with DN32 cells. (B) Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type mice, incubated for 24 h with BMS212122, and washed. The exogenous antigens ovalbumin or α-galcer were added as indicated. Splenocytes were then co-cultured with autoreactive 24.8 NKT cells (left), DN32 NKT cells (center), or CD4+ cells from an OT-II transgenic mouse (right). *, P < 0.05. Results are representative of two independent experiments. (C) CD11c+ splenocytes were incubated for 24 h with BMS212122, DMSO, or 9-fluorenyl carboxylic acid, washed, and co-cultured with 50,000 24.8 NKT cells per well. *, P < 0.005; **, P < 0.05 compared with DMSO values. Results are representative of five independent experiments. (D) CD11c+ splenocytes were incubated for 4 d with BMS212122 or DMSO, pulsed with the indicated concentrations of α-galcer, washed, and co-cultured with DN32 NKT cells (E/T = 100,000:30,000). *, P < 0.05. (E) 30,000 CD11c+ splenocytes incubated for 24 h with BMS212122 or DMSO were washed and co-cultured with 100 μg/ml ovalbumin and 100,000 CD4+ cells from an OT-II transgenic mouse. Values are ±SD.