Figure 1.
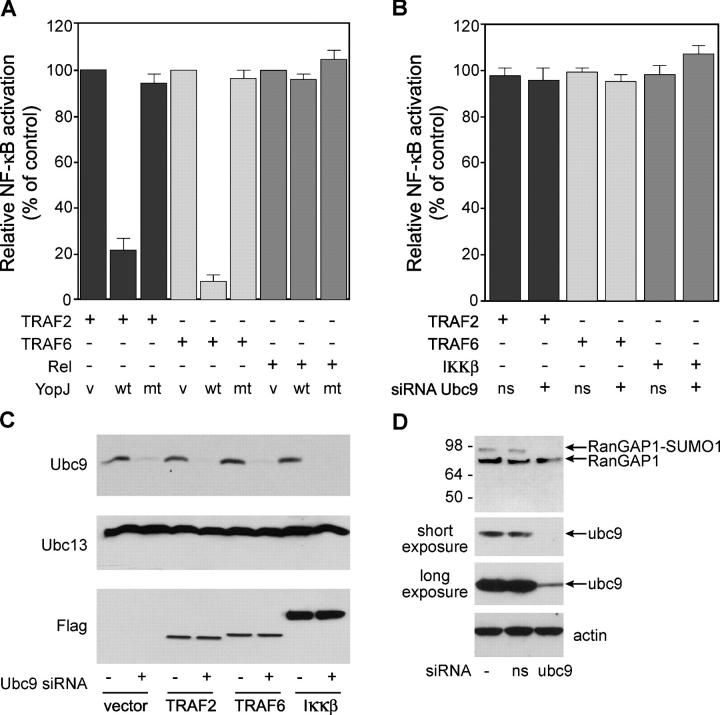
YopJ inhibits NF-κB activation by diverse stimuli. (A) HEK 293T cells were transfected with an NF-κB–dependent reporter gene, the indicated activator of NF-κB signaling, and either control empty vector (v), WT YopJ (wt), or YopJ mutant C172A (mt). NF-κB activation was measured by dual-luciferase reporter assay after 36 h and is presented as a percentage of the activity induced by TRAF2 (lane 1), TRAF6 (lane 4), or Rel (lane 7) alone. Expression of YopJ, TRAF2, TRAF6, and Rel was confirmed by Western blotting (not depicted). (B) 293T cells that were transfected with siRNAs targeting Ubc9 or a nonspecific siRNA (ns) were cotransfected with Flag-tagged TRAF2, TRAF6, or IKKβ, and NF-κB activation was measured after 36 h. NF-κB activity is presented as a percentage of the activity induced by either TRAF2, TRAF6, or IKKβ in the absence of any siRNA oligos. (C) Cell lysates from B were Western blotted for Ubc9 (top), Ubc13 (middle), and TRAF2, TRAF6, or IKKβ (bottom). (D) 293T cells that were transfected with or without siRNAs targeting Ubc9 were cotransfected with RanGAP1. Modification of RanGAP1 by SUMO-1 was measured after 36 h by immunoblotting with RanGAP1 antibody (top). The actin blot shows equal protein loading (bottom).