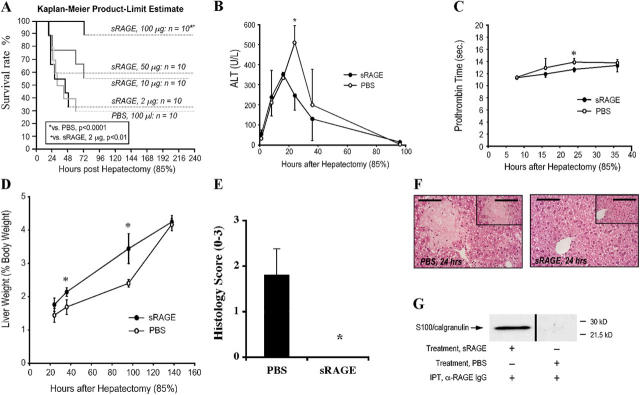
Figure 2.
Administration of sRAGE improves survival and enhances regeneration after massive hepatectomy. Male C57BL/6 mice were subjected to 85% hepatectomy in the presence of the indicated once daily dose of sRAGE or vehicle, PBS. (A) Kaplan-Meier Product Limit Estimate. The times of death were recorded for mice undergoing hepatectomy in the presence of sRAGE versus vehicle, and survival was plotted. Survival curves for sRAGE, 100 μg/d- and PBS-treated mice, reflect the same animals as in Fig. 1 A. (B–D) Indices of injury and regeneration. At the indicated times, plasma or hepatic remnant was retrieved and analyzed for ALT (B) and Prothrombin Time (C). (D) Liver weight/body weight ratios are shown. (B and C) n = 3–8 mice per condition. (D) n = 10 (PBS) or n = 27 (sRAGE) mice per condition. (B–D) *, P < 0.05. (E and F) Histology. Hepatic remnants were retrieved and grading was performed based on the percentage of necrosis as described before; mean ± standard error is shown. (E) n = 5 mice per condition. *, P < 0.05. (F) Representative sections from PBS- and sRAGE-treated mice at 24 h are illustrated. Bar, 80 μm (inset) 160 μm. (G) Immunoprecipitation. 16 h after 85% hepatectomy, plasma from sRAGE- or PBS-treated mice was retrieved and subjected to immunoprecipitation using rabbit anti-RAGE IgG. Immunoprecipitated material was subjected to blotting using anti-S100/calgranulin IgG. Plasma was pooled from n = 3 sRAGE- or n = 3 PBS-treated plasma for immunoprecipitation studies.