Figure 1.
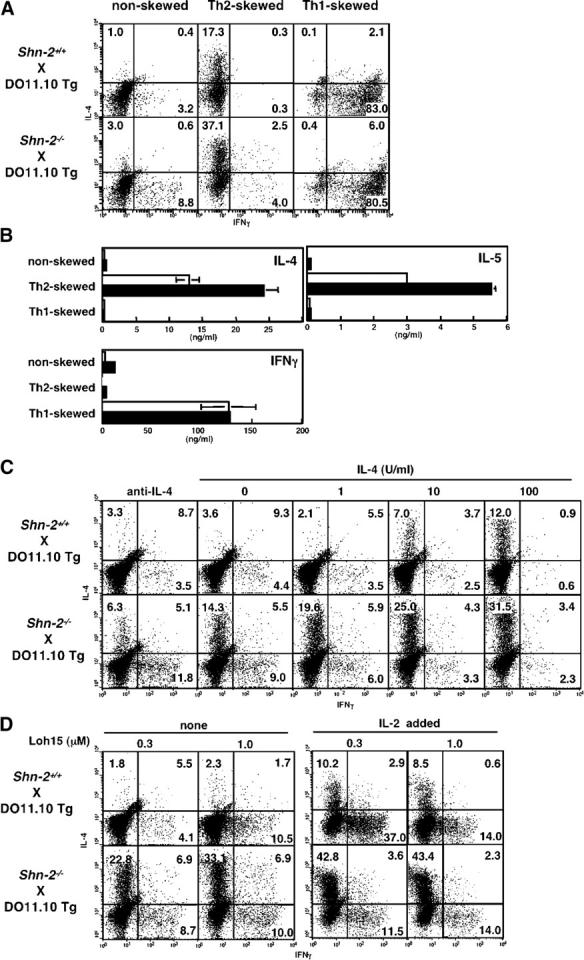
Enhanced Th2 cell differentiation in Shn-2−/−× DO11.10 TCR Tg T cells. (A) Naive (CD44low) CD4 T cells from Shn-2−/−× DO11.10 Tg mice were purified by cell sorting and stimulated with antigenic OVA peptide (Loh15: 0.1 μM) and irradiated BALB/c APCs for 5 d. Th2 cell–skewed (IL-4 with anti–IL-12 mAb and anti–IFN-γ mAb), Th1 cell–skewed (IL-12 with anti–IL-4 mAb), and nonskewed (IL-2 with anti–IL-4 mAb, anti–IL-12 mAb, and anti–IFN-γ mAb) conditions were used. Intracellular staining was performed with FITC-conjugated anti–IFN-γ mAb and PE-conjugated anti–IL-4 mAb. Under the typical Th2 cell–skewed conditions, the levels of Th2 cell differentiation in five experiments were 17.5 ± 2.9% in Shn-2 + / + cultures and 38.0 ± 11.8% in Shn-2−/−cultures. P < 0.006. (B) A portion of the same differentiated cell cultures used in A were restimulated with antigenic peptide and APCs for 24 h, and the concentrations of cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-γ) in the culture supernatant were determined by ELISA. (C) Naive (CD44low) CD4 T cells from Shn-2−/−× DO11.10 Tg mice were stimulated with a specific OVA peptide (Loh15: 0.1 μM) and irradiated normal BALB/c APCs in the presence of indicated doses of IL-4. Intracellular staining profiles of IFN-γ and IL-4 are shown with percentages of cells in each area. (D) Purified naive (CD44low) CD4 T cells were stimulated with indicated doses of specific OVA peptides (Loh15: 0.3 and 1.0 μM) and irradiated BALB/c APCs in the presence or absence of 30 U/ml of exogenous IL-2. Two independent experiments were performed with similar results.
