Figure 5.
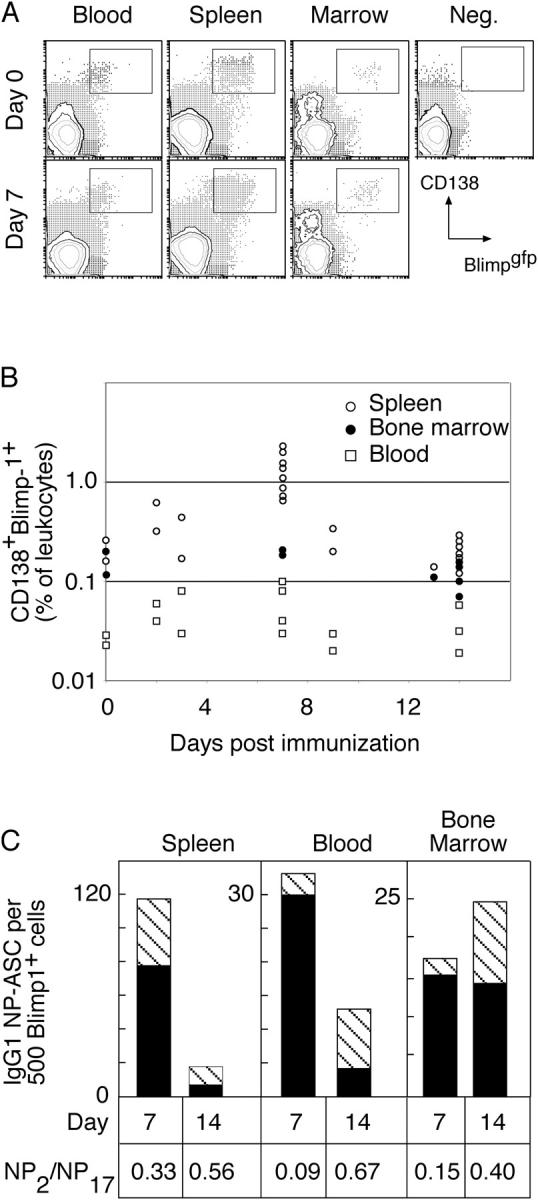
ASCs in blood after immunization revealed by expression of blimp-1. (A) Mice with GFP targeted to one allele of the blimp-1 locus were immunized, and blood, spleen, and bone marrow were collected at the indicated times. Flow cytometric analysis of leukocytes revealed populations of GFP+CD138+ cells in all tissues. (B) The frequency of such cells in individual mice is indicated as a percentage of total blood leukocytes for the different tissues. Data from spleen and bone marrow have been reported previously (reference 31) and are shown here for comparative purposes only. (C) GFP+CD138+ cells were purified by sorting and assessed for the frequency of NP-binding IgG1 ASCs, comparing spleen, blood, and bone marrow populations from the same times. In each case, 500 sort-purified cells were placed in ELISPOT wells coated with either high or low haptenated proteins to detect total or high affinity NP-specific IgG1 ASCs, respectively. The number of spots of each type is plotted and represents the average compiled from four experiments at day 14 and three at day 7, each experiment using tissue pooled from two to four mice. The number of total IgG1 anti-NP ASCs per 500 sorted cells is indicated by the height of the column and the number of high affinity ASCs by the striped section of each column. Unimmunized mice (n = 3) showed no NP- specific IgG1 ASCs in any location. The proportion of total ASCs with high affinity is calculated as NP2/NP17 ASCs. The change in ratio between days 7 and 14 within each population is significantly different (P < 0.05, Student's t test) although the differences between populations at each time are not significantly different.
