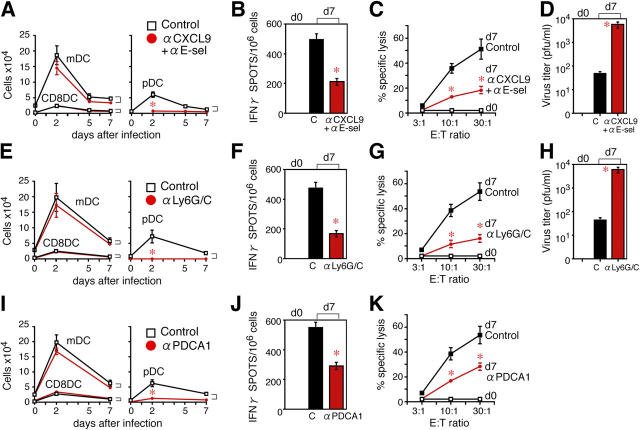
Figure 3.
In vivo depletion of pDCs impairs CTL-mediated virus eradication. The effect of anti-CXCL9 and anti–E-selectin Abs on (A) the numbers of B220− LNDCs (mDCs and CD8α+ DCs) and B220+ pDCs in PLNs after HSV infection, (B) the numbers of IFN-γ+ spots produced by PLN CD8+ T cells, (C) the specific lysis in vitro by PLN CD8+ T cells, and (D) the virus titer in PLNs. The effect of anti-Ly6G/C Ab on (E) the numbers of B220− LNDCs (mDCs and CD8α+ DCs) and B220+ pDCs in PLNs after HSV infection, (F) the numbers of IFN-γ+ spots produced by PLN CD8+ T cells, (G) the specific lysis in vitro by PLN CD8+ T cells, and (H) the virus titer in PLNs. The effect of anti–PDCA-1 mAb on (I) the numbers of B220− LNDCs (mDCs and CD8α+ DCs) and B220+ pDCs in PLNs after HSV infection, (J) the numbers of IFN-γ+ spots produced by PLN CD8+ T cells, and (K) the specific lysis in vitro by PLN CD8+ T cells. Representative data from three independent experiments are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 6 or n = 5 for anti–PDCA-1 mAb experiments. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test, comparing mice treated with control and blocking Abs.