Figure 5.
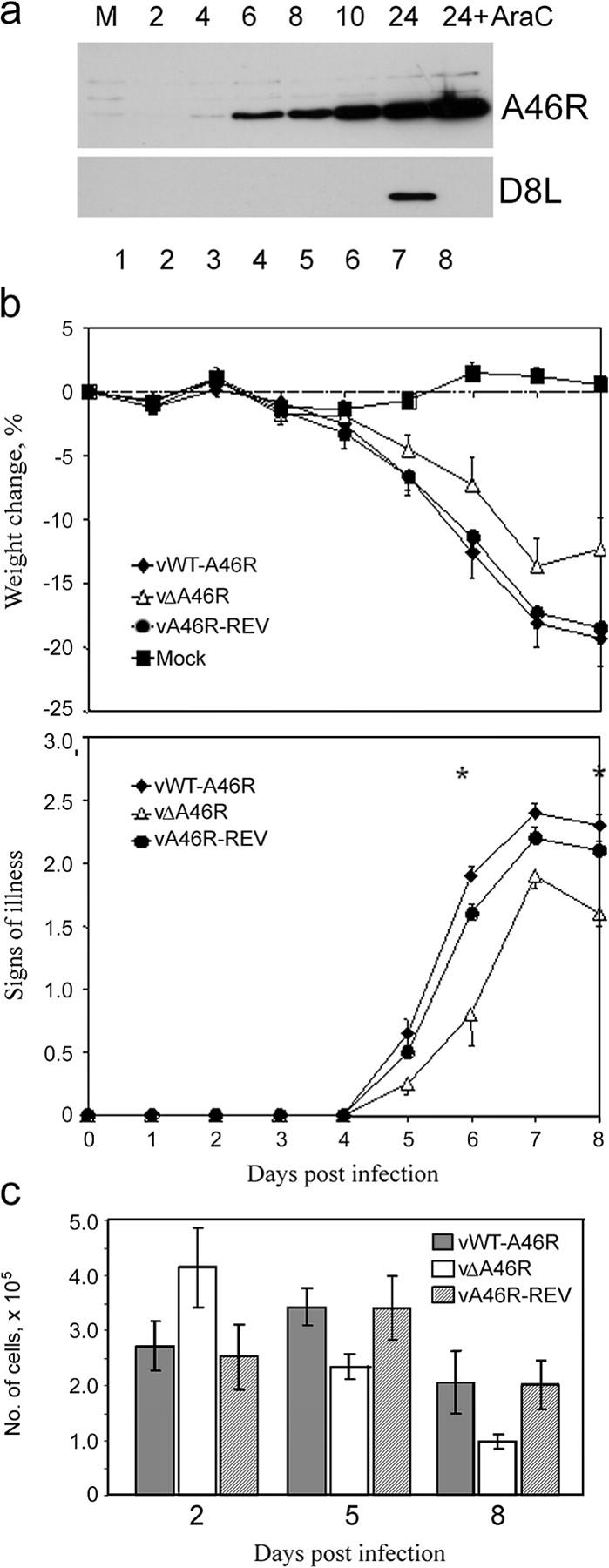
A46R is expressed early during virus infection and contributes to virus virulence. (a) BSC-1 cells were mock infected (M) or infected with VV Western reserve (MOI = 5) in the absence or presence of 40 μg/ml cytosine β-D-arabinofuranoside (AraC). Cells were harvested at the indicated times (h) after infection, and lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting, using either anti-A46R (top) or anti-D8L (bottom) Ab. (b) A46R contributes to virus virulence. Groups of 15 female, 6-wk-old Balb/c mice were infected intranasally with 5 × 103 PFU of vWT-A46R, vΔA46R, or vA46R-REV. Each day, animals were weighed and the signs of illness were scored. Data are presented as the mean weight of each group of animals compared with the mean weight of the same group on day 0 (top graph), and the mean signs of illness score (bottom graph). Error bars are SEM. Asterisks represent days on which there was a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05; Student's t test) between the vWT-A46R and both control groups. (c) Number of cells recruited to the lungs of VV-infected mice. On days 2, 5, and 8 after infection, mice were killed, lungs were harvested, and cell suspensions were prepared. The total number of viable lung cells per animal was determined by Trypan blue exclusion. Data are means ± SEM.
