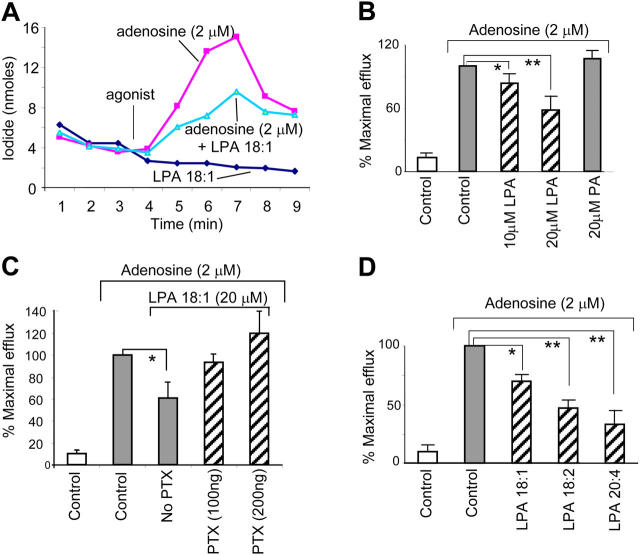
Figure 2.
LPA inhibits CFTR-dependent iodide efflux through LPA2 receptor–mediated Gi pathway. (A) Representative ADO-activated CFTR-mediated iodide efflux in Calu-3 cells treated with LPA 18:1 (20 μM, BSA-complexed). (B) ADO-activated iodide efflux in LPA 18:1- or PA-pretreated Calu-3 cells. Note: the peak efflux is shown (5-min time point). (C) Calu-3 cells were pretreated with PTX (100 and 200 ng) for 24 h at 37°C and subjected to iodide efflux activated by ADO in the presence of LPA 18:1 (20 μM). (D) Peak efflux of iodide in response to ADO in Calu-3 cells that were treated with various LPA analogs (20 μM). Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4–6 each group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.