Figure 3.
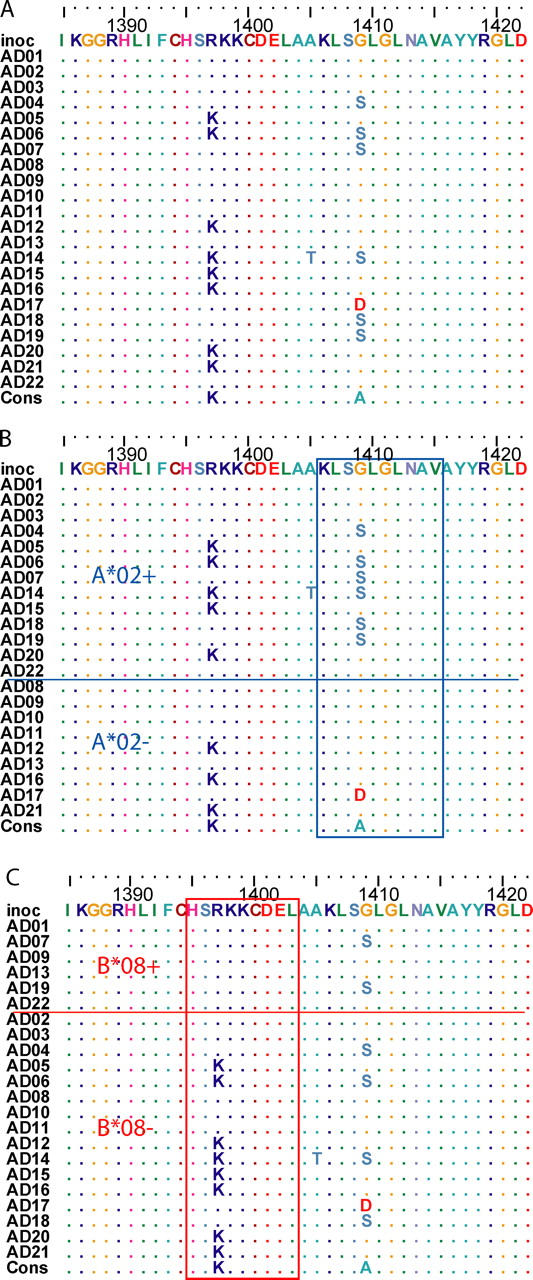
Escape versus reversion in the presence versus absence of the restricting HLA allele. (A) Amino acid alignment of a region in NS3 (positions 1388 to 1431 relative to the H77 polyprotein (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. AF009606) showing sites with polymorphism. Study subjects are listed in arbitrary order. Identity to the inoculum sequence (“inoc”) is indicated by “.”. (B) Sorting the subjects by the presence of HLA A*02, G1409S substitution in the 4th position of a frequently recognized HLA A*02-restricted epitope at 1406–1415 is limited to subjects having the HLA A*02 allele. The subtype 1b consensus sequence for this epitope is shown below the alignment, and has been shown to be recognized as readily as the prototype (subtype 1a) KLVALGINAV sequence (27). Subject AD17 (HLA A*01, A*11) had G1409D substitution, the impact of which on recognition is unknown. (C) Variation resulting in reversion to a HLA B*08-restricted epitope. Sorting the subjects by presence of HLA B*08, R1397K substitution in the 3rd position of a frequently recognized HLA B*08- restricted epitope at 1395–1403 is limited to subjects lacking the HLA B*08 allele. The inoculum sequence differs from the prototypical epitope (HSKKKCDEL) at the 3rd position. Reversion to consensus (and the prototype epitope) occurred only in study subjects lacking the HLA B*08 allele.
