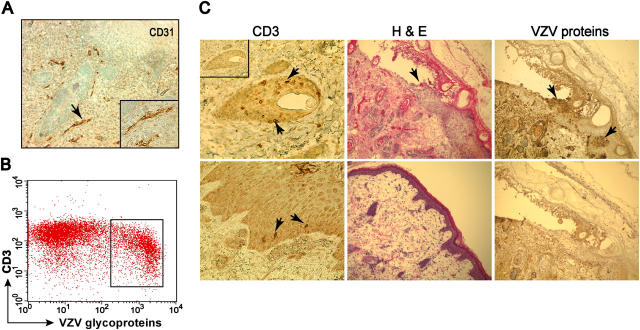
Figure 1.
Transfer of VZV by CD3+ T cells. Column-purified CD3+ T cells from tonsils were cocultured with VZV-infected HEL cells for 48 h before i.v. transfusion into SCID mice with human skin xenografts. Skin implants were harvested at various times after T cell transfer, snapped frozen, and sectioned. (A) Human fetal skin xenografts differentiated in SCID mice at 4 wk expressed human CD31 on the endothelial cells (magnification: 100×; insert, 200×). (B) 15–30% of tonsillar T cells used to inject SCIDhu mice expressed VZV glycoproteins as shown in a representative flow cytometric analysis. (C) CD3+ T cells were detected around hair follicles and along basement membranes 24 h after i.v. injection (left, arrows; insert, rabbit IgG control); VZV-induced cytopathology was shown by hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) stain 21 d after T cell transfer compared with uninfected control (middle) and by anti-VZV IgG (brown, top right; bottom right, VZV nonimmune IgG control) (magnification: left, 400×; middle and right, 100×).