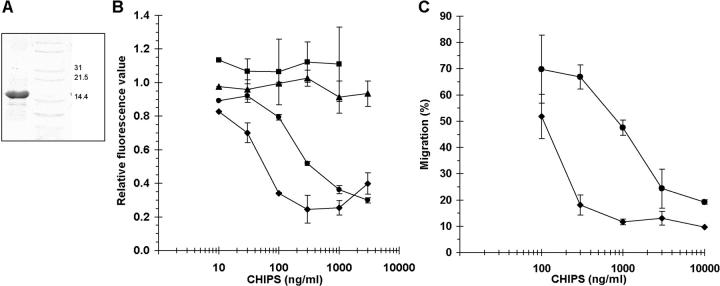
Figure 1.
Purified CHIPS inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis toward C5a and fMLP. (A) CHIPS was purified by ligand dye chromatography and gel filtration from S. aureus culture supernatant. Active fractions were pooled and concentrated. SDS-PAGE revealed a band of ∼15 kD. The right lane represents a marker. (B) CHIPS affects C5aR and FPR expression on neutrophils in a dose-dependent fashion. Binding of BODIPY-formylated peptide (♦) and anti-C5aR mAb (•) to their receptors on neutrophils is inhibited after 30 min of incubation with different concentrations of CHIPS, whereas binding of anti-PAFR (▪) and anti–IL-8R (▴) mAb is not inhibited. Data are expressed as fluorescence values compared with neutrophils without CHIPS and are mean ± SEM of three separate experiments. (C) CHIPS inhibits chemotaxis of neutrophils toward 10−7 M fMLP (♦) and 10−10 M C5a (•) after incubation of neutrophils with different concentrations of CHIPS. Data are expressed as the percentage of migrated neutrophils added to the upper compartment of the transwell chemotaxis chamber and are mean ± SEM of one representative experiment (n = 2–4). Migration of untreated neutrophils was 79% for C5a and 85% for fMLP.