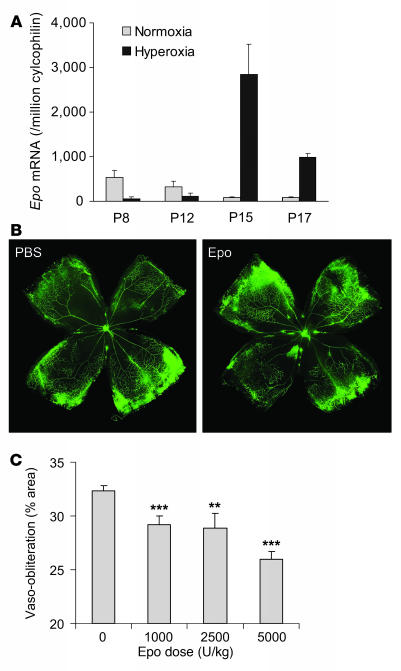
Figure 1. Epo treatment prevents oxygen-induced retinal vessel loss in a dose-dependent manner.
(A) Real-time PCR quantification of Epo mRNA expression in age-matched mouse retinas under normoxia or hyperoxia treatment; copy number of Epo mRNA/106 copies of cyclophilin A control mRNA at P8, P12, P15, and P17 (n = 6 per group). (B) Representative retinal whole-mounts showing area of vaso-obliteration after 18 h of oxygen exposure and i.p. injection (P6 and P7) of Epo (right) or saline control (left). Original magnification, ×5. (C) Dose response of Epo protection against retinal vaso-obliteration at P8 (with i.p. injections at P6 and P7) (saline, n = 40; Epo 1,000 U/kg, n = 12; 2,500 U/kg, n = 7; 5,000 U/kg, n = 16) **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.