Figure 6.
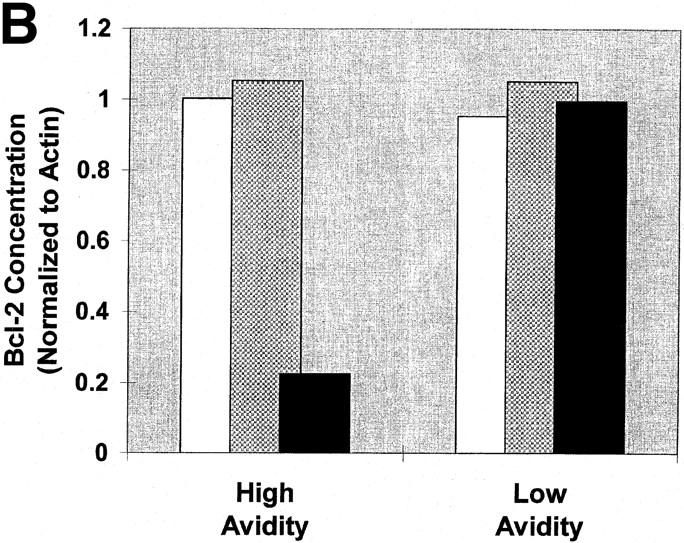
The induction of apoptotic death is associated with a decrease in Bcl-2 levels. High and low avidity CTLs were cultured in the presence of immobilized Dd (0.5 μg/well) pulsed with either 50 μM or 0.005 μM I10 peptide, or unpulsed. After 24 h, CTLs were harvested and solubilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors. Lysates were analyzed by Western blot analysis for expression of Bcl-2. Actin was used as a control to ensure equivalent loading among the samples. High avidity CTLs stimulated with high peptide–MHC determinant density have significantly decreased expression of Bcl-2 compared with CTLs stimulated with low peptide–MHC determinant density. Low avidity CTLs stimulated with these same conditions showed no change in expression of Bcl-2. (A) Visualization of FITC-conjugated antibodies after transfer of protein bands to nitrocellulose. In this experiment, Bcl-2 is not demonstrable in the high avidity CTL line after culture with high I10 peptide despite a relatively higher amount of cell extract loaded on that lane (as assessed by the densities of the actin bands). (B) In a replicate experiment, binding of FITC-conjugated antibodies was quantitated and the binding to Bcl-2 normalized by comparison with binding to actin. Quantitation in several experiments showed that Bcl-2 in CTLs cultured with high peptide decreased to between 0 and 35% of the Bcl-2 present in controls. White bars, no peptide; gray bars, 0.005 μM; black bars, 50 μM.

