Figure 1.
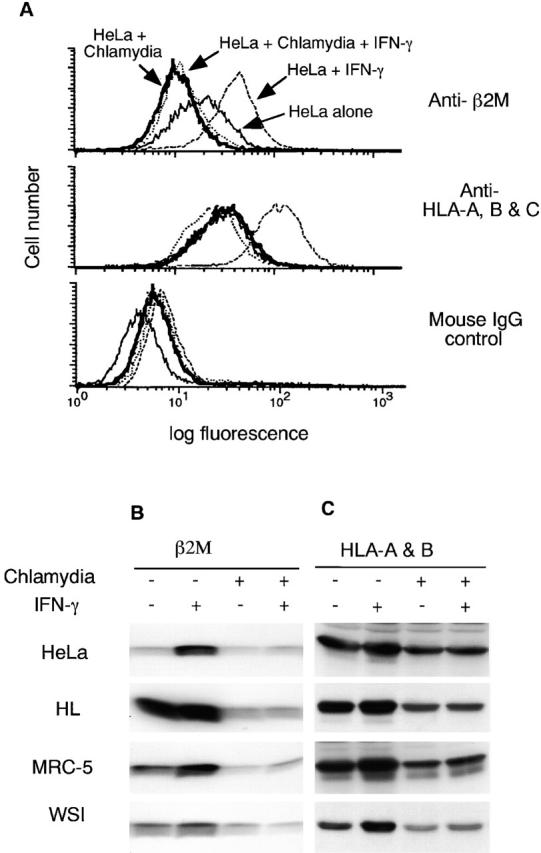
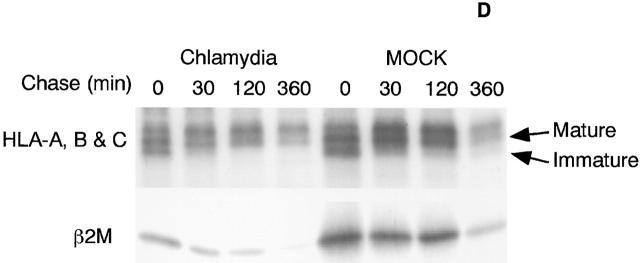
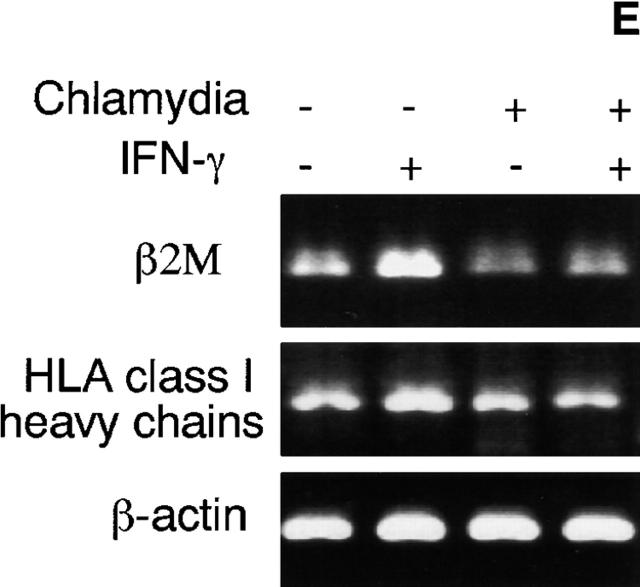
Chlamydia inhibits both constitutive and IFN-γ–inducible MHC class I expression in infected cells. HeLa cells with or without chlamydial infection were stimulated with IFN-γ or unstimulated and collected for flow cytometry (A), Western blot (B and C), and RT-PCR (E) analysis. Chlamydia prevents both constitutive and IFN-γ–inducible HLA-A, -B, and -C heavy chain and β2M surface expression (A). Chlamydia suppresses the total cellular protein level of both constitutive and IFN-γ–inducible β2M (B) and HLA-A and -B heavy chains (C) in various human cell lines. Chlamydia inhibits the mRNA expression of both MHC class I heavy chains and β2M (E). For pulse–chase labeling experiment (D), HL cells with or without chlamydial infection were metabolically labeled with S35–methionine/cysteine for 30 min, and the pulsed cell samples were aliquoted and chased for various times as indicated. Mature or immature bands correspond to proteins resistant or sensitive to EndoH digestion as determined in a separate experiment (data not shown).