Figure 1.
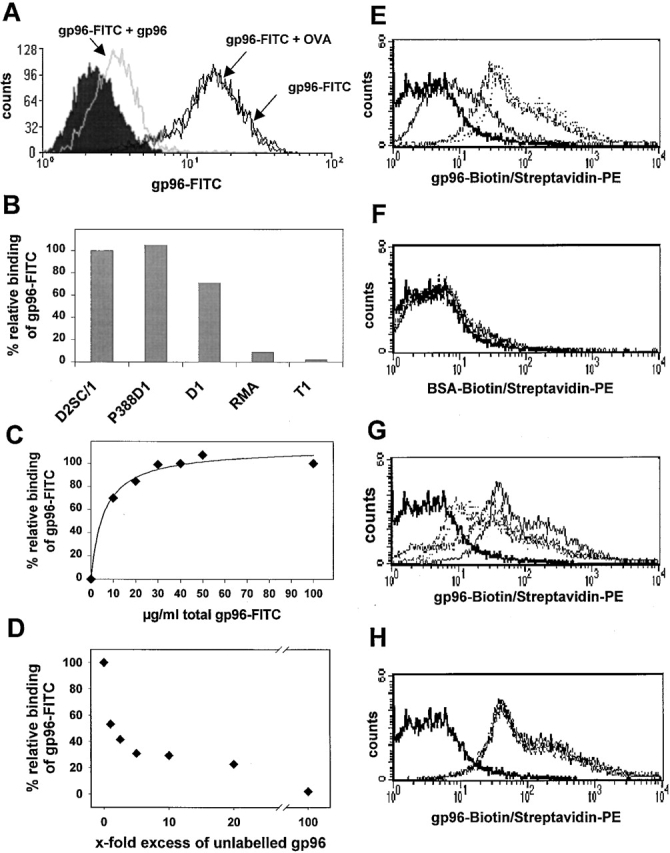
Specific binding of gp96-FITC to APC cell lines and BMDCs. Binding of 3 μg gp96-FITC to 105 D2SC/1 cells was performed, always at 4°C, in 100 μl IMDM containing 10% FCS. This binding could be competed by a 10-fold excess of unlabeled gp96, but not OVA. (A) Specific binding of gp96-FITC was observed on D2SC/1 (DC progenitor), P388D1 (macrophage), and D1 (DC), but not on RMA and T1 cells. (B) Binding could be saturated at ∼30 μg/ml for 105 D2SC/1 cells (C) and competed almost completely by a 100-fold excess of unlabeled gp96. (D) Binding is given as relative values, where 100% represents maximum binding of gp96-FITC. The concentration values shown give total concentration of gp96-FITC added to the cells. (E) Binding of 1 μg (bold line), 5 μg (broken line), and 10 μg (dotted line) gp96-biotin/streptavidin-PE to immature BMDCs from C57BL/6 mice. (F) No binding was observed for BSA-biotin/streptavidin-PE. Binding of 10 μg gp96-biotin (bold line) to BMDC is competed in a similar fashion to D by unlabeled gp96 (G), but not by unlabeled BSA (H).
