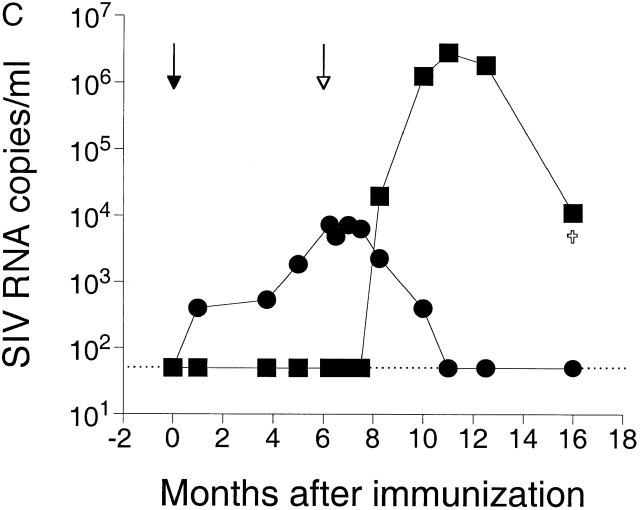
Figure 2.
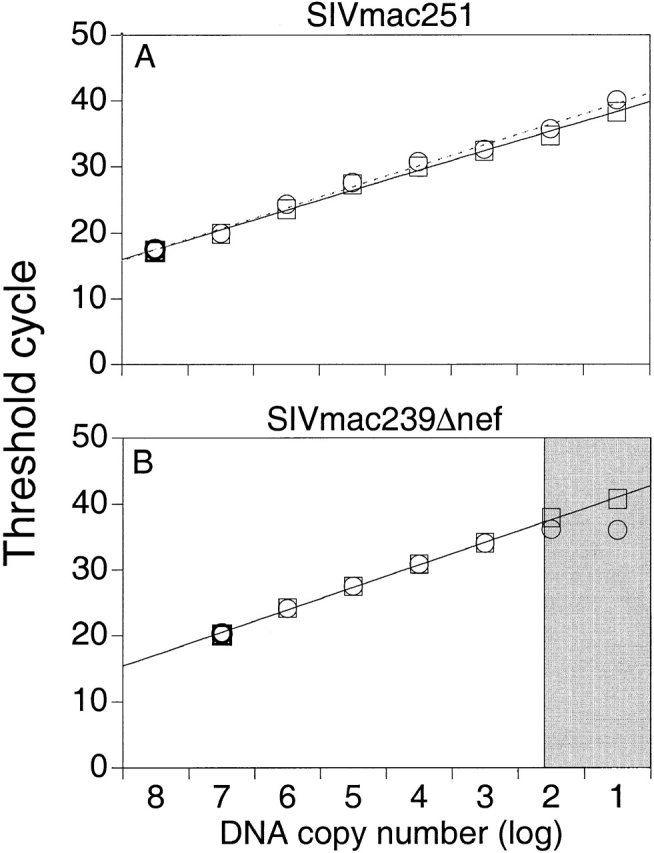
(A) Discriminatory ability of real-time PCR for differential amplification. Amplifications of SIVmac251 were performed using a serial dilution of SIVmac251 DNA standard with (○) and without (□) the addition of 108 copies of noncomplimentary SIVmac239Δnef DNA standard. Mean values of reactions performed in duplicate are shown. The dotted and solid lines indicate the linear standard curves as results of amplifications with and without the addition of noncomplimentary DNA, respectively. (B) Amplifications of SIVmac239Δnef were performed using a serial dilution of SIVmac239Δnef DNA standard with (○) and without (□) the addition of 108 copies of noncomplimentary SIVmac251 DNA standard. The linear standard curve for amplification of SIVmac239Δnef DNA alone is shown in black. The gray section indicates the area where the ratio of copies of SIVmac239Δnef to copies of SIVmac251 is ≥1/106. (C) Measurement of SIV RNA in plasma after immunization with SIVmac239Δnef and challenge with SIVmac251. Rhesus macaque 1510 was immunized with SIVmac239Δnef on day 0 (black arrow) and then challenged with SIVmac251 at 25 wk (white arrow). SIVmac239Δnef RNA (•) and SIVmac251 RNA (▪) in plasma were quantified using real-time PCR for differential amplification. The limit of sensitivity of the viral load assay is indicated by the dotted line.