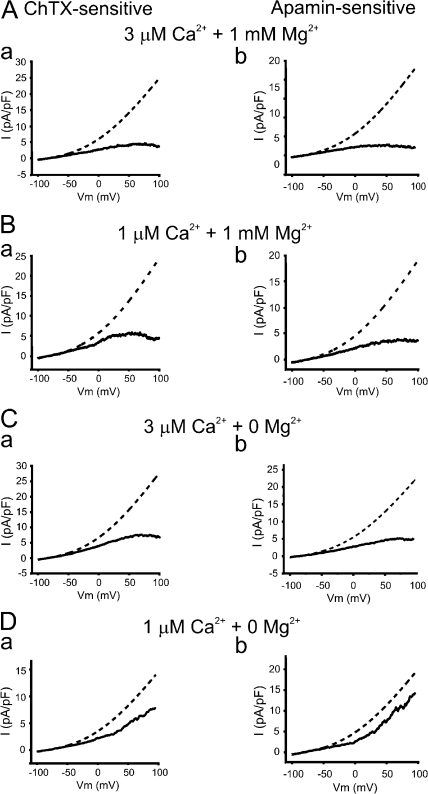
Figure 3.
The inward rectification of IKCa and SKCa is caused by intracellular Mg2+ and Ca2+. (A and B) Mean IKCa (a) and SKCa (b) currents (filled lines) elicited by voltage ramp protocol in AECs dialyzed with 1 mM free Mg2+ and (A) 3 μM free Ca2+ (n = 6 and 5, respectively) or (B) 1 μM free Ca2+ (n = 5 and 5). Predictions from the GHK constant field equation (dashed lines) were obtained by fitting the mean inward currents of IKCa (a) and SKCa (b) of AECs (filled lines) in each condition. (C and D) Similar to A and B except that endothelial cells were dialyzed with a Mg2+-free ([Mg2+] = 0) pipette solution containing either (C) 3 μM free Ca2+ (n = 4 and 4) or (D) 1 μM Mg2+ (n = 4 and 5 for IKCa and SKCa, respectively). Predictions from the GHK constant field equation (dashed lines) were obtained by fitting the mean inward currents of IKCa (a) and SKCa (b) of AECs (filled lines) in each condition. Currents were evoked by a 200-ms voltage ramp protocol from −100 to + 100 mV (HP = −60 mV). [K]o, 6 mM; [K]i, 150 mM; and PK, 8.7872 E − 14 and 2.1968 E − 14 for IKCa and SKCa, respectively.