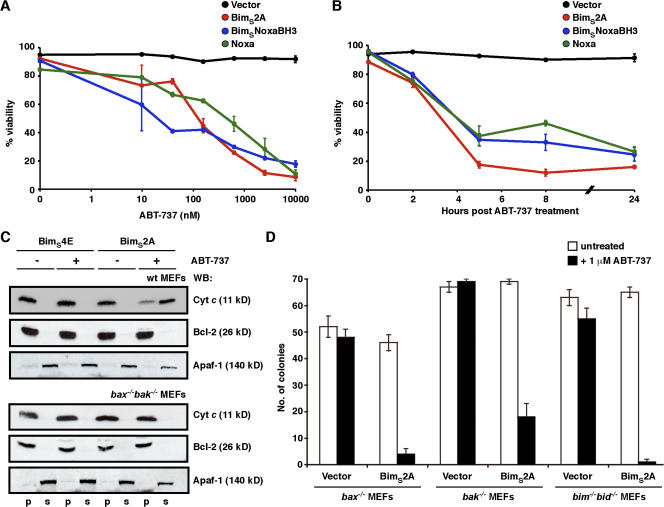
Figure 4.
BimS2A efficiently inactivates Mcl-1 to induce cell killing. (A) BimS2A sensitizes cells to ABT-737, a BadBH3 mimetic. The viability of MEFs stably infected with the vector control or ones expressing BimS2A, BimSNoxaBH3, or Noxa was determined 24 h after treatment with 0–10 μM ABT-737. Although ABT-737, which targets Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and Bcl-w, was inert on its own, the three Mcl-1–selective BH3-only proteins were equipotent at cooperating with ABT-737 to efficiently kill cells. (B) The kinetics of killing with 1 μM ABT-737 were comparable regardless of whether Mcl-1 was degraded (with Noxa or BimSNoxaBH3) or neutralized (with BimS2A). (C) BimS2A promotes Bax/Bak-mediated cytochrome c release only when combined with ABT-737. Equivalent lysates prepared from wild-type (top) or bax−/−bak−/− (bottom) MEFs stably expressing the inert BimS4E or the Mcl-1–specific BimS2A were fractionated after incubation in vitro with 5 μM ABT-737 (+). Only the combination of BimS2A and ABT-737 caused cytochrome c release, which was abrogated in the absence of Bax and Bak (bottom). Blots for Bcl-2 (pellet fraction; p) and Apaf-1 (soluble fraction; s) served as markers for the subcellular fractionation. (D) Only when combined with ABT-737 does the Mcl-1–specific BimS2A kill cells, either through Bax or Bak without the need for the putative activator BH3-only proteins (Bim and Bid). Data in A, B, and D are means ± SD (error bars) of at least three experiments, whereas C is from a representative experiment.