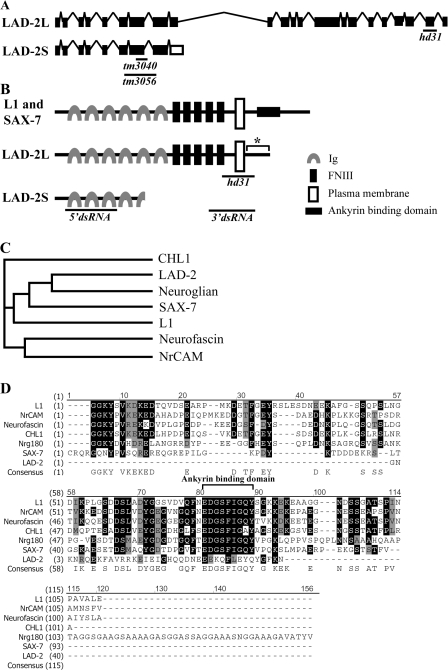
Figure 1.
The lad-2 gene encodes a noncanonical L1CAM homologue in C. elegans. (A) Genomic organization of the alternatively spliced isoforms (not drawn to scale). The black boxes represent exons; the inverted Vs represent introns; and the open boxes represent an alternatively spliced exon. Black bars mark the end points of the hd31, tm3040, and tm3056 deletions. (B) A schematic of the protein structure of L1, SAX-7, and the LAD-2 isoforms LAD-2L and LAD-2S. Anti–LAD-2 antibodies were generated against the LAD-2 cytoplasmic tail (asterisk). Black bars mark the LAD-2 regions that are removed by the hd31 deletion or targeted by the dsRNAs in RNAi experiments. 5′ dsRNA targets the 5′ sequence that is shared by both LAD-2L and LAD-2S, whereas 3′ dsRNA targets the 3′ sequence that is unique to LAD-2L. (C) A phylogenetic tree of the L1CAM extracellular domains shows that LAD-2 is most closely related to the D. melanogaster neuroglian. (D) An amino acid sequence alignment of the L1CAM cytoplasmic tails reveals that LAD-2 has a divergent cytoplasmic tail.