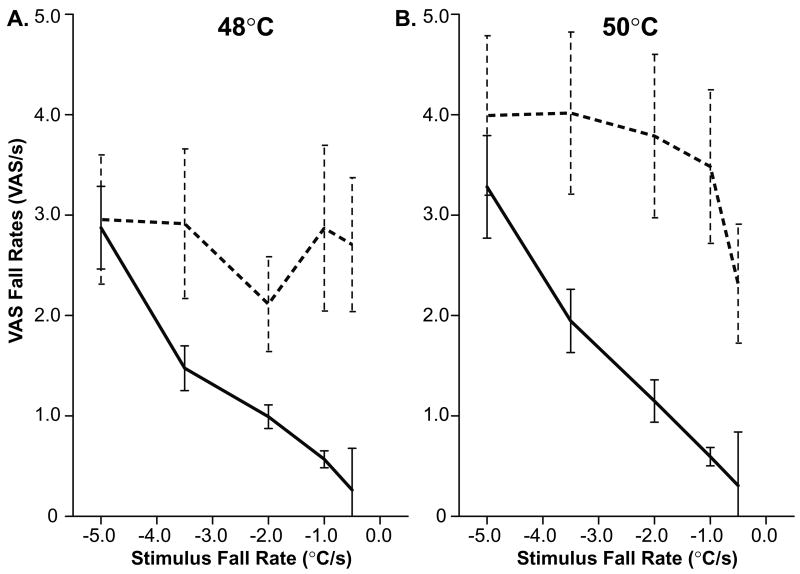
Figure 5. Actual Psychophysical Fall Rates (dashed lines) are Significantly More Rapid than Expected Fall Rates (solid lines).
Expected fall rates were modeled using a linear relationship between the stimulus fall rate and perceived intensity fall rate. These expected data were plotted against observed VAS fall rates (averaged across subjects) for both 48°C and 50°C stimuli (a and b, respectively). Note that due to offset analgesia there is very little change in VAS fall rate regardless of stimulus fall rate. Additionally, at the fastest fall rate (−5.0°C/s) actual and expected fall rates begin to converge.