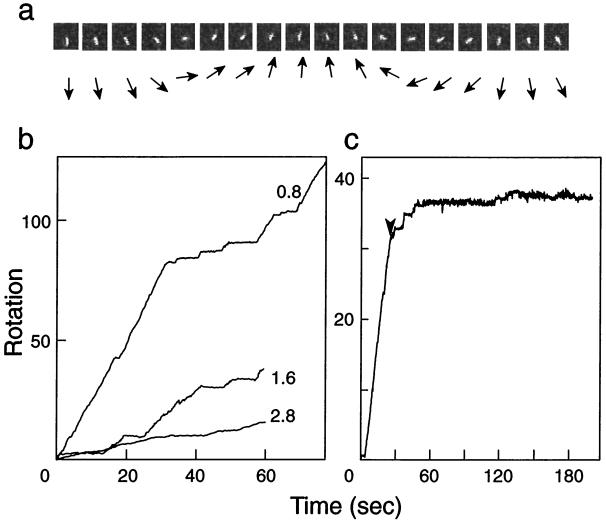
Figure 1.
Rotation of an actin filament attached to the γ-subunit of E. coli F1-ATPase. (a) Typical sequential video images (left to right) of a rotating actin filament attached to the engineered enzyme (αHis-tag/γSer193Cys) in 5 mM Mg-ATP; the filament length between rotation axis and the tip was 2.1 μm, and the image interval was 100 msec. The directions of the actin filaments are shown schematically by arrows below the video images. (b) Examples of the rotation of actin filaments dependent on time. The rotations of actin filaments (0.8, 1.6, and 2.8 μm) were followed in the presence of 5 mM Mg-ATP. (c) Effect of azide on the rotation of a 2.0-μm actin filament. A reaction mixture containing 1 mM sodium azide was slowly (≈2 μl/sec) introduced into the cell at the time indicated by the arrowhead.