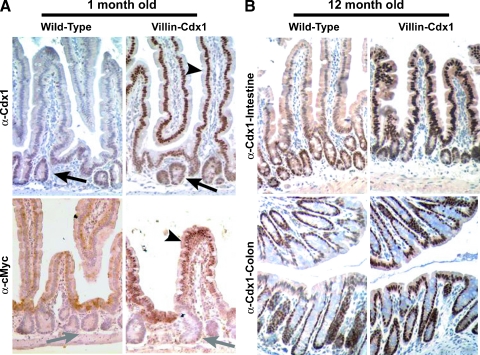
Figure 2.
Cdx1 ectopic expression in the small intestine villi and colon surface epithelium of Villin-Cdx1 transgenic mice. The small intestine and colon from transgenic or littermate control mice were excised at 1 and 12 months, fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde, then processed for immunohistochemical studies. (A) Anti-Cdx1 antibody (CPSP) demonstrating that Cdx1 protein is limited to the crypt epithelial cells in 1-month-old wild-type mice (arrow). In contrast, in villin-Cdx1 transgenic mice, we see darkly stained nuclei in the upper crypt and in the villus epithelial cells (arrowhead). A mouse monoclonal antibody against the human cMyc-tag does not recognize endogenous mouse cMyc in the crypt cells of 1-month-old wild-type offspring (gray arrow) but detects nuclear-localized transgene expression in the small intestinal villi of transgenic mice (arrowhead). (B) These patterns of Cdx1 expression persist in 1-year-old wild-type and transgenic animals. Cdx1 protein is limited to the colon crypts of 1-year-old wild-type mice but is highly expressed in the colon surface epithelium of transgenic mice.