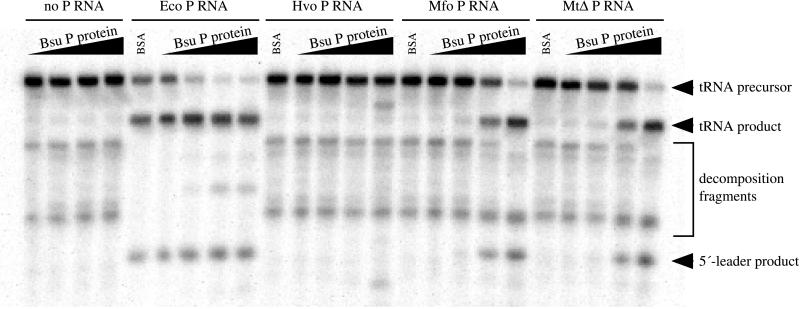
Figure 6.
Reconstitution of active chimeric holoenzymes. RNase P RNAs from E. coli (Eco, 38 μg/ml), H. volcanii (Hvo, 170 μg/ml), M. formicicum (Mfo, 60 μg/ml), or M. thermoautotrophicum ΔH (MtΔ, 33 μg/ml) were assayed for RNase P activity in the presence of 0, 0.1, 1, or 10 μg/ml B. subtilis RNase P protein (increasing protein concentration indicated by black wedges above the reaction lanes). Specific RNase P cleavage products are indicated by black arrowheads. The E. coli RNase P RNA is somewhat active by itself under these conditions, but activity is enhanced by the inclusion of the B. subtilis RNase P protein. The M. thermoautotrophicum and M. formicicum RNase P RNAs are not active in the absence of protein under these conditions but were activated by inclusion of the B. subtilis RNase P protein. Correct processing by the H. volcanii RNase P RNA was not observed under these conditions in either the presence or absence of the B. subtilis RNase P protein. However, a specific inappropriate cleavage was generated at the highest concentration of protein; the nature of these products and the apparent miscleavage have not been determined.