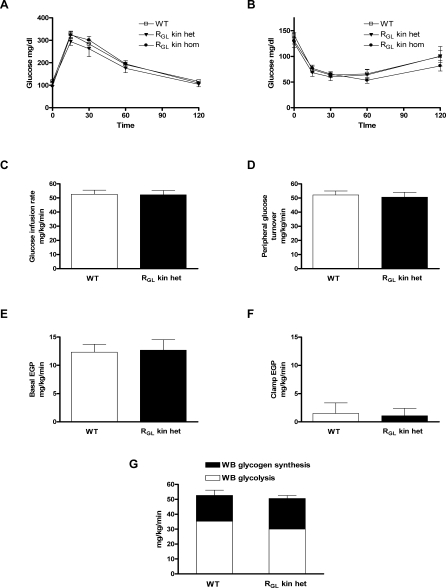
Figure 6. Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity in RGL Knock-in Mice.
(A) Glucose tolerance following intraperitoneal glucose (2 mg/g body weight) administration in WT, RGL knock-in heterozygous (RGL kin het), and RGL kin homozygous (RGL kin hom) mice.
(B) Plasma glucose response to intraperitoneal insulin (0.75 mU/g body weight) in WT-, RGL knock-in heterozygous (RGL kin het)-, and RGL knock-in homozygous (RGL kin hom) mice. Peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity were assessed by means of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in WT and RGL kin het mice (C–G). Glucose infusion rates (C); peripheral glucose turnover (D); and basal (E) and suppressed (F) endogenous glucose production (EGP) during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps.
(G) Whole body (WB) glycolysis and glycogen synthesis were measured during the clamps.
Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM for 6–9 mice per treatment group.