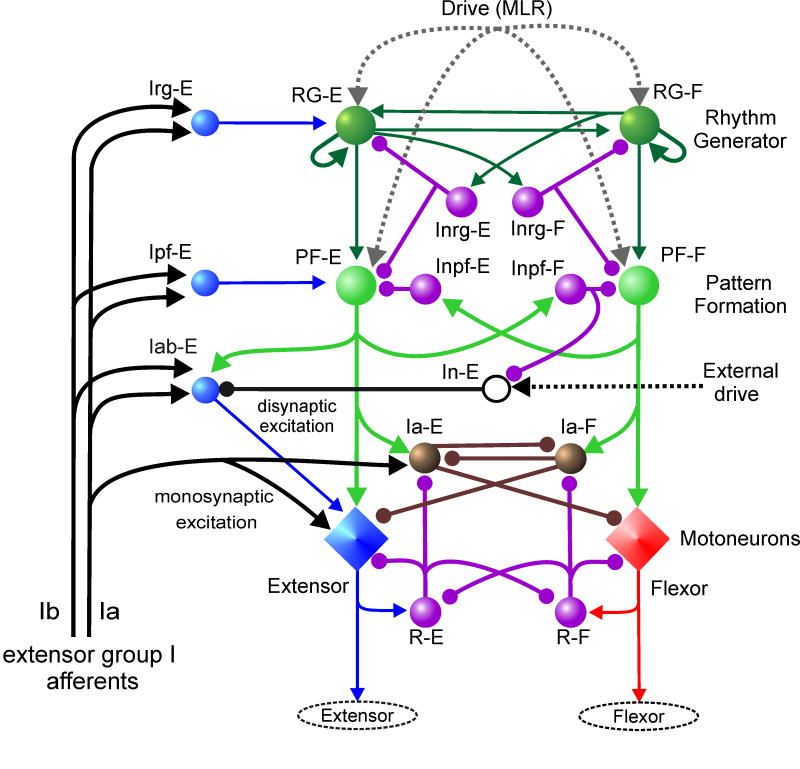
Fig. 2. Rybak-McCrea CPG model.
Detailed schematic of a computational model of the of the spinal circuitry with the two-level CPG. Rhythm Generator (RG) and Pattern Formation (PF) networks representing the two levels of the CPG are labelled on the right. The excitatory RG populations reciprocally inhibit each other via the inhibitory Inrg populations. The PF populations reciprocally inhibit each other through the Inpf inhibitory populations. The RG-E and RG-F populations have recurrent excitatory connections and excitatory connections between the half-centers. Locomotion is initiated by a tonic excitatory drive (MLR) to both the RG and PF populations. The locomotor rhythm and the durations of flexor and extensor phases are determined by the RG network which controls the activity of the PF network by a combination of direct excitation and inhibition mediated by the Inrg populations. PF population activity produces a phase-specific activation of the corresponding group of synergist motoneuron pools. Phase-dependent inhibition of motoneurons is produced by the Ia-E and Ia-F populations whose activity is regulated by excitation from the PF network and inhibition from Renshaw cells (R-E and R-F) as well as mutual inhibitory connections between the Ia populations. Afferent input from extensor muscle spindle (Ia) and tendon organ (Ib) afferents to the spinal circuits are shown on the left. Activity in Ia afferents evokes monosynaptic excitation of synergist (extensor) motoneurons and disynaptic inhibition of antagonists. During locomotion, extensor group Ia and Ib afferents access the CPG at the RG and PF levels through the Irg-E and Ipf-E populations, respectively. Extensor motoneurons also receive a phase-dependent excitation from the Iab-E population whose activity is augmented by group I sensory input during the extensor phase. The Iab-E population is inhibited at rest by tonic drive from the In-E population. This inhibition is removed during the extension phase by inhibition from the Inpf-F population. Further details in Rybak et al. (2006 a, b).