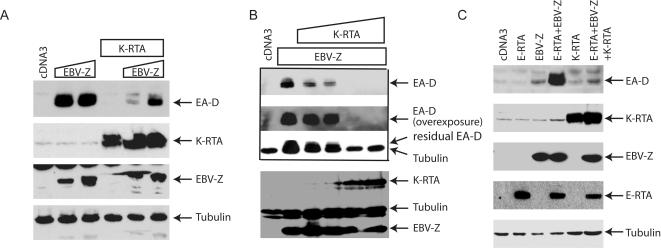
Figure 2. K-RTA inhibits EBV-Z-mediated EBV lytic gene expression.
A. K-RTA inhibits EBV-Z-mediated EBV lytic gene expression. EBV-Z expression plasmid (0, 0.1, and 0.2 µg) plus K-RTA (0.2 µg) were transfected into BRLF1KO (EBV+/KSHV−) cells in 6-well plate as shown on the top. Lysates were used for western blot analysis 24 hours later. The same membrane was stripped and reprobed with other antibodies. The identity of proteins is as shown. B. Dose-dependent inhibition of EBV-Z-mediated lytic gene expression by K-RTA. Fix amount of EBV-Z expression plasmid (0.1 µg) plus various amounts of K-RTA (0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4 µg) were transfected into BRLF1-KO (EBV+/KSHV−) cells in 6-well plate as shown on the top. Lysates were used for western blot analysis. Same cell lysates were used. C. K-RTA inhibits the synergistic activation of EA-D. EBV-Z expression plasmid (0.025 µg), E-RTA (0.1 µg), and K-RTA (0.2 µg) were transfected with different combinations into BRLF1-KO cells as shown on the top. The same cell lysates were used for western blot analysis. The identity of proteins is as shown.