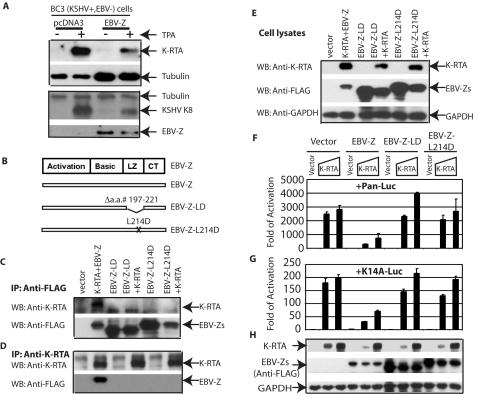
Figure 5. EBV-Z inhibits KSHV lytic gene expression.
A. EBV-Z inhibits KSHV lytic gene expression. BC3 (KSHV+/EBV−) cells were transfected with CD4 expressing plasmid along with EBV-Z or vector plasmids. The transfected cells were isolated and equally split into two wells: one well of the cells was treated with TPA for 24 hours. Cell lysates were used for western blot analysis. B. Schematic of EBV-Z functional domains and mutants. The activation domain, basic region (DNA binding domain), leucine zipper region (LZ), and a region of unknown structure at the C terminus (CT) are shown. The drawing is not on scale. In Panels C, D, and E, 293T (EBV−/KSHV−) cells were transfected with various expression plasmids as shown on the top. FLAG-EBV-Z, and its mutants were used. Cell extracts from these transfected cells were immunoprecipitated with either anti-FLAG (for EBV-Z) (Panel C) or anti-K-RTA (Panel D). The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using the indicated antibodies. In Panel E, whole cell lysate was used for western blot analyses. The identity of the respective proteins is denoted. In Panels F, G, and H, 293T (EBV−/KSHV−) cells were used. Panel F, KSHV Pan-promoter reporter construct (Pan-luc) and CMV-β-gal expression plasmid were cotransfected with 400 ng of EBV-Z or its mutant expression plasmids, together with 0, 20, 50 ng of K-RTA expression plasmids respectively as shown on the top. In Panel G, KSHV K14-promoter reporter construct (K14A-luc) and CMV-β-gal expression plasmid were cotransfected with 100 ng of EBV-Z or its mutant expression plasmids, together with 0, 10, 20 ng of K-RTA expression plasmids respectively as shown on the top. Luciferase activity was normalized by β -galactosidase activity. The relative folds of activation of promoter constructs are shown with standard deviations. One representative of three independent experiments is shown. Panel H, cell lysates from Panel F were used for western blot analysis. The same membrane was stripped and reprobed with other antibodies. The identity of proteins is as shown.