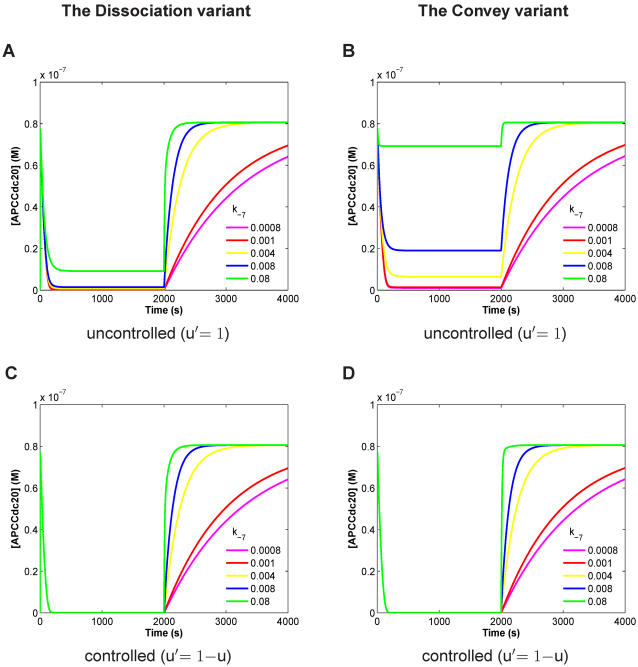
Figure 2. Dynamical behavior of APC:Cdc20 concentration versus time for the Dissociation variant (A, C) and the Convey variant (B, D) each in the uncontrolled (A, B) and the controlled (C, D) case.
Calculation results are presented for different values of the rate k−7 in [s−1 >(dissociation of MCC:APC) between 0.0008 and 0.08, because k−7 is unknown and crucial for model behavior, as indicated. The APC:Cdc20 concentration should be close to zero before attachment and should rise quickly after attachment. Spindle attachment occurs at t = 2000s (switching parameter u from 1 to 0). For the uncontrolled case (A, B), both variants cannot explain the checkpoint behavior; and the Convey variant is even less satisfying compared to the Dissociation variant. In the controlled case (C, D), both variants fully inhibit APC:Cdc20 before attachment and both show fast switching recovery for high k−7 values. The controlled Convey variant (D) is slightly faster (by about 5 mins) in switching compared to the controlled Dissociation (C) variant. Parameters setting according to Table 1 and Table 2.