Figure 1.


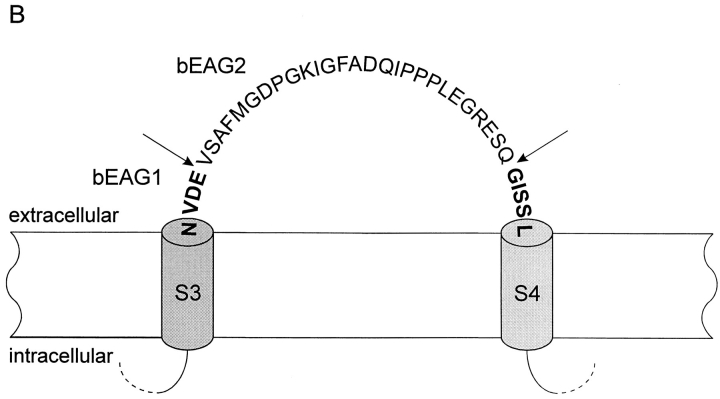
Alignment of amino acid sequences of EAG channel polypeptides. Sequences: bovine EAG splice variant 2 (bEAG 2); rat EAG (rEAG; Ludwig et al., 1994), Drosophila EAG (DmEAG; Warmke et al., 1991) and human EAG (hERG; Warmke and Ganetzky, 1994). (A) Transmembrane regions (S1–S6), the pore region, and the putative cyclic nucleotide-binding site are overlined. Consensus sites for N-linked glycosylation of bEAG2 are labeled by an asterisk. Consensus sites for phosphorylation of bEAG2 by CaM kinase II and cAMP/cGMP-dependent kinases are labeled by open arrowheads and open circles, respectively. Amino acid position is indicated at the right hand side. Identical residues are depicted as white letters on black, conservative substitutions as black letters on gray. Note the insertion of 27 amino acid residues (position 318–344) in bEAG2, that is missing in bEAG1. (B) Amino acid sequence of the S3–S4 linker of bEAG1/2. A topological model of the S3–S4 region of bEAG channels is shown. Residues common to both bEAG1 and bEAG2 are depicted in bold letters. The sites of insertion of 27 additional residues in bEAG2 are indicated by arrows.