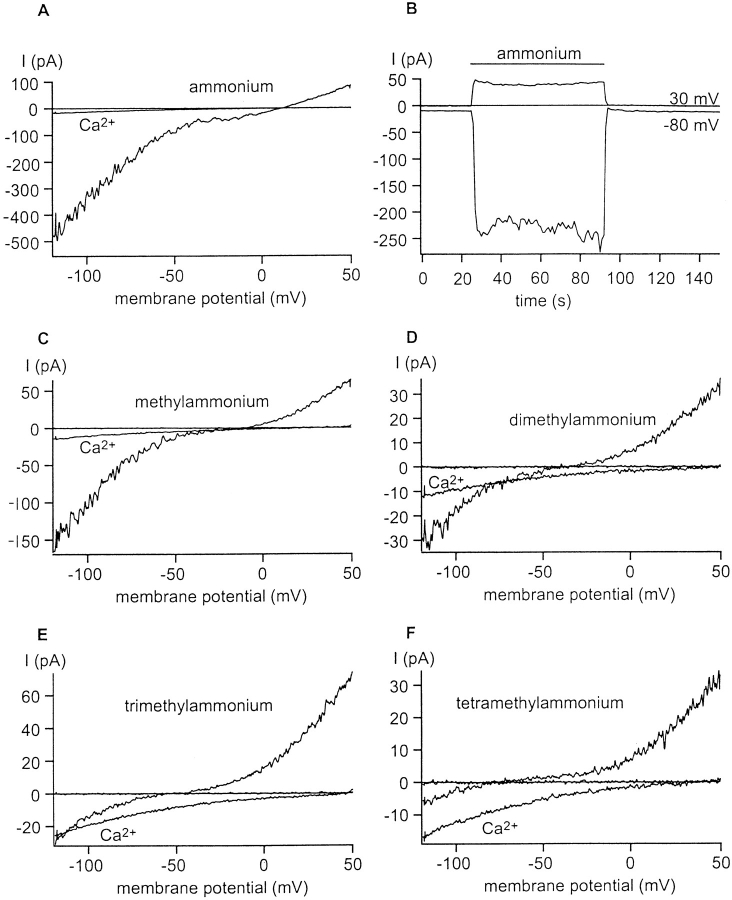
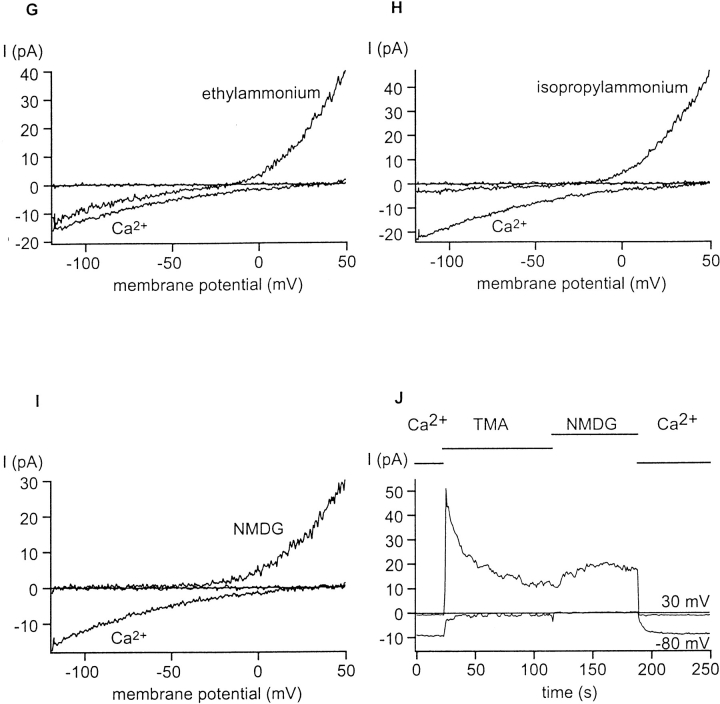
Figure 2.
Permeability of CRAC channels to organic cations. CRAC channels were activated during whole-cell dialysis with Na+ aspartate. The external solution contained 1 μM Ca2+ and 150 mM X+, where X+ is ammonium (A and B), methylammonium (C), dimethylammonium (D), trimethylammonium (E), tetramethylammonium (F and J), ethylammonium (G), isopropylammonium (H), and NMDG+ (I and J). Most panels illustrate currents using voltage ramps as in Fig. 1; note that the current amplitude scales vary. For these panels, three ramp traces show, including one before activation of CRAC channels, Ca2+ currents through CRAC channels with 20 mM [Ca2+]o, and monovalent currents upon lowering [Ca2+]o to 1 μM. (B and J) Current amplitudes at −80 and +30 mV before and after changing the bath solution from 20 mM Ca2+ to 1 μM Ca2+ containing ammonium (B) or TMA+ followed by NMDG+ (J). The bars above the current correspond to the main external cation. Note that the NH4 + currents are sustained in B. In I and J, there are no detectable inward currents carried by NMDG+. TMA+ carries a small but detectable inward current (F and J).