Figure 3.
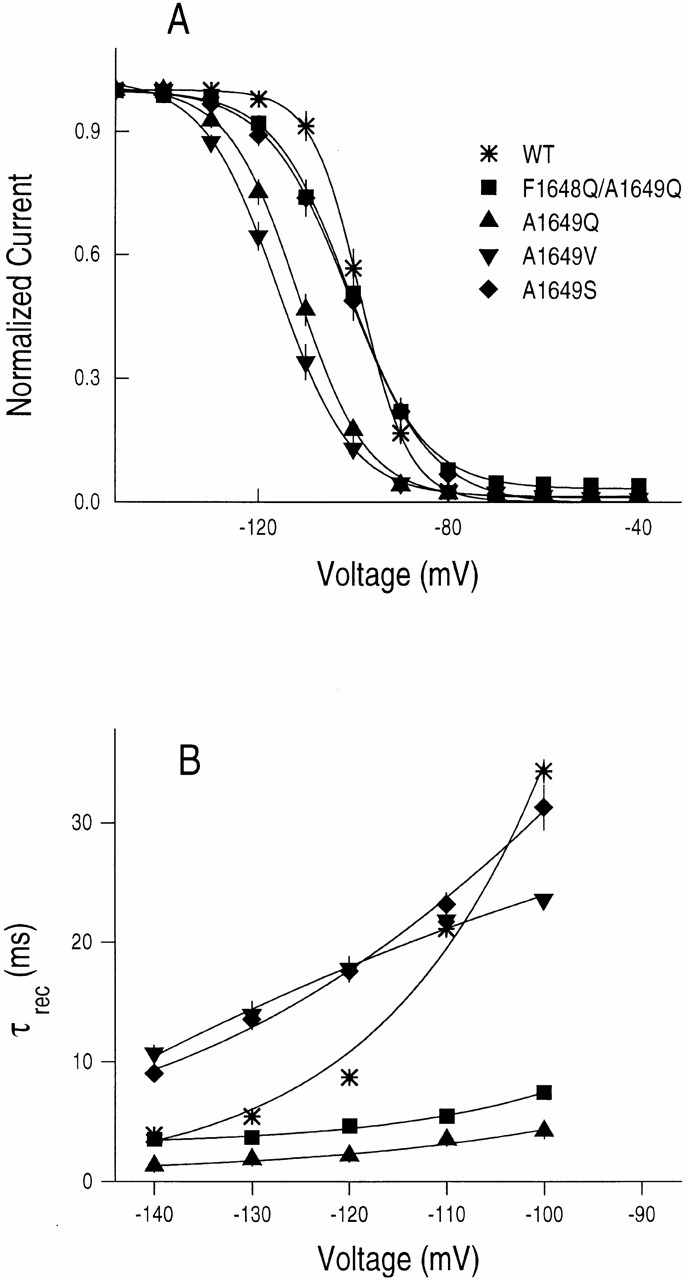
(A) Steady state inactivation for WT, F1648Q/A1649Q, A1649S, A1649V, and A1649Q channels. Currents were measured at a test potential of −30 mV after 500-ms conditioning pulses at indicated voltages from a holding potential of −120 mV. Each peak current was normalized by maximal peak current and fit by the Boltzmann equation I/I max = 1/{1 + exp[(V − V 1/2)Z m F/RT]}, where I is the current at each voltage, I max is the maximum current, V 1/2 is the half-maximal voltage and Z m is the apparent gating valence in equivalent electronic charges (e o) (Table I). (B) Time constants for recovery from inactivation (τrec). Inactivation elicited by 15-ms prepulses to 0 mV from a holding potential of −120 mV, followed by a given recovery potential for a variable time interval, and tested at 0 mV. The normalized peak currents of the test pulse were plotted as a function of time (t) between the pulses. Such plots were fit with single exponential functions to determine the recovery time constant (τrec) at each potential, and τrec values are from I test /I prepulse = 1 − exp(t/τrec) plotted as a function of recovery potential.
