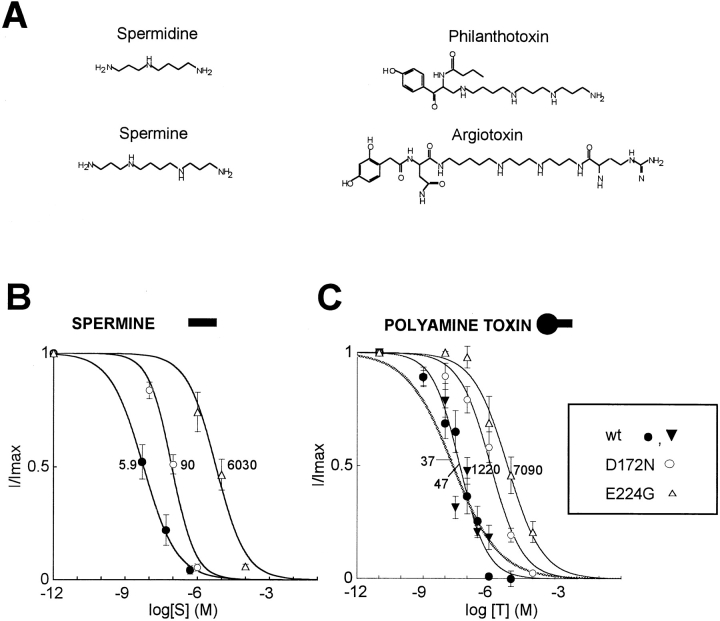
Figure 1.
Polyamines and polyamine toxins. (A) Chemical structures of spermine, spermidine, and the polyamine toxins philanthotoxin and argiotoxin. (B) Dose–response curves of block of wild-type Kir2.1, D172N, and E224G by spermine (left) and philanthoxin (•, ○, and ▵) or argiotoxin (▾, right). Each data point is the mean ± SEM for n = 4–6 patches. The giant excised inside-out patches were all superfused for >5 min with Mg- and polyamine-free bath solution before spermine or phi-lanthotoxin exposure. Currents were measured at the end of a 200-ms voltage clamp pulse to +40 mV, from a holding potential of −40 mV. Superimposed curves are least-squares fits to a Hill equation, with the numbers indicating K 0.5 values. The Hill coefficients ranged from 0.62 to 0.90 for spermine and from 0.55 to 0.70 for philanthoxin.