Figure 2.
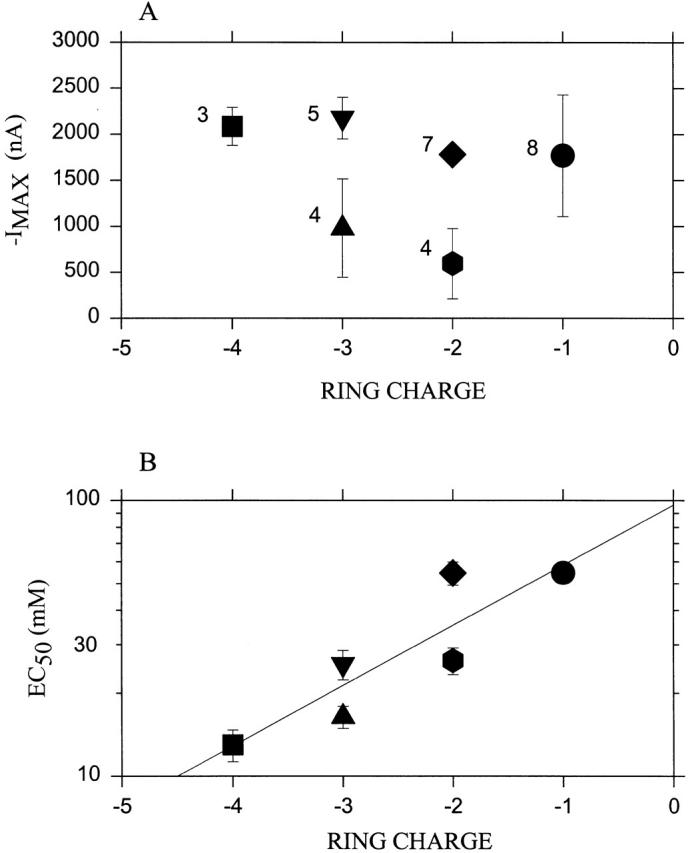
Responses of complexes of subunits mutated in the Glu ring. Oocytes were injected with all four types of subunits. In all cases, α contained the mutation T244C; this is designated α− if E241 is not also mutated, and α0 if in addition E241 is mutated to Q (i.e., the superscript indicates the charge of the residue in the position of the Glu ring). Wild-type β is designated β−; β with the mutation E252 to Q is designated β0; and β with the mutation E252 to K is designated β+. Wild-type γ is designated γ0. Wild-type δ is designated δ−, and δ with the mutation E255 to Q is designated δ0. The complexes tested were: α− 2β−γ0δ− (i.e., a pseudo wild type with only αT244 mutated to C; ring charge, −4; square); α− 2β0γ0δ− (ring charge, -3; up triangle); α− 2β−γ0δ0 (ring charge, −3; down triangle); α0 2β−γ0δ− (ring charge, −2; diamond); α− 2β+γ0δ− (ring charge, −2; hexagon); and α0 2β0γ0δ− (ring charge, −1; a circle). (A) The average maximum current (−IMAX) obtained from the fit of the Hill equation to the responses at various concentrations of ACh. (B) The average EC50 obtained from the fit of the Hill equation. The least-squares linear fit to the log(EC50) is shown. In each case, the abscissa is the sum of the charges in the ring. The numbers of independent experiments are indicated next to the symbols. The bars represent the standard errors of the means.
