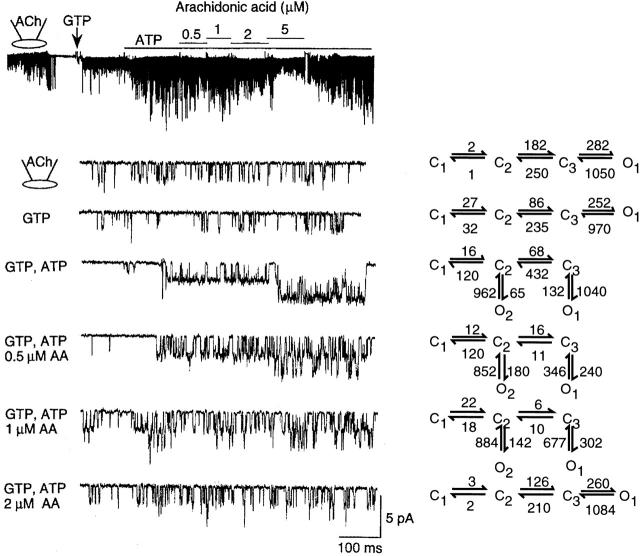
Figure 9.
Inhibitory effect of arachidonic acid on the KACh channel. A cell-attached patch was formed with ACh in the pipette. After forming an inside-out patch, 100 μM GTP was added to activate the KACh channels. ATP (4 mM) was then added to further increase the channel activity. In the presence of GTP and ATP, 0.5 μM AA was applied and its concentration increased stepwise to 5 μM, and then washed off. Expanded current tracings are shown for different experimental conditions. For each condition, channel data were fitted to one of two kinetic schemes (Fig. 2 B) and transition rates between all connected states were determined. Averaged transition rates determined from three similar patches are shown on the left. The linear scheme was used whenever the open time constants of the two open states were close (i.e., within 15% of each other).