Figure 3.
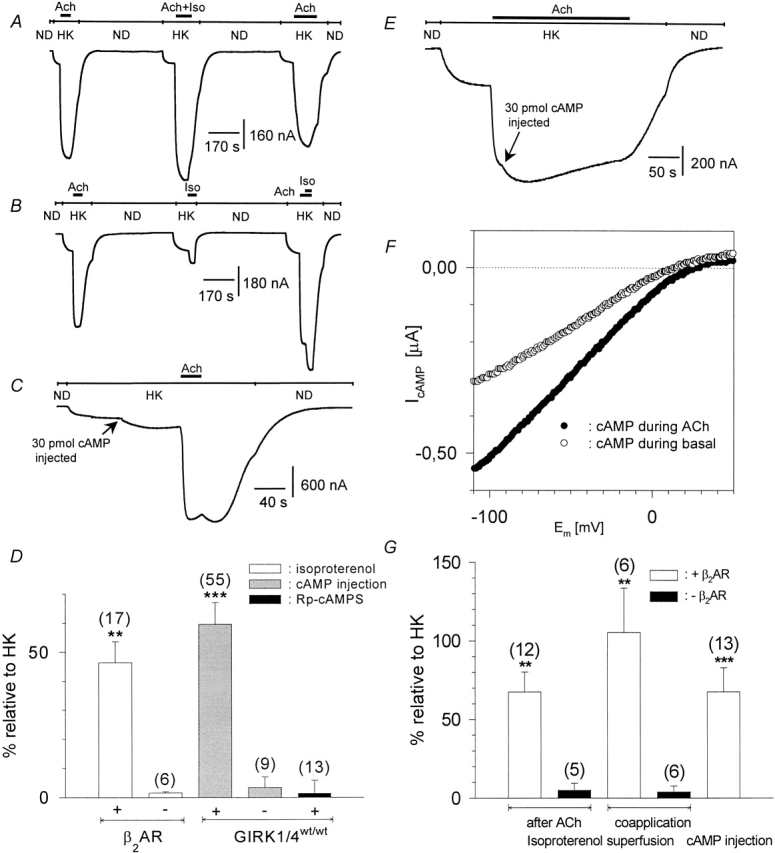
β2-adrenergic facilitation of heterologously coexpressed GIRK currents and cAMP effects in Xenopus laevis oocytes. (A) Original current trace recorded at a membrane holding potential of −80 mV. ND and HK denote changes of the superfusion medium from ND96 to HK, bars denote superfusion with agonists. (B) Same as in A, but Iso was applied alone or during ACh. (C) Same as in A, but 30 pmol cAMP was injected during HK before ACh superfusion. (D) Statistics of the effects of isoproterenol superfusion and/or cytosolic injection of cAMP and Rp-cAMPS on basal current amplitude, expressed as percentage of basal I HK. Calculated average values ± SEM are shown; the number of individual cells is given in parenthesis. (** and ***) Mean value deviates significantly (P < 0.01 and 0.001) from the corresponding control group (i.e., oocytes not expressing heterologous β2AR in the case of Iso effects) or cAMP injection into native oocytes in the case of cAMP effects. (Left to right) Iso-induced current on basal HK (with or without coexpressed β2AR), 30–60 pmol cAMP injection during basal HK, cAMP injection into native oocytes, injection of 30–60 pmol Rp-cAMPS during basal HK. (E) Same as in C, but cAMP was injected during ACh. (F) Current–voltage relation of the cAMP-induced currents as measured by a triangular voltage pulse (f = 1 Hz). (○) Current induced by cytosolic cAMP injection on basal current, obtained by subtraction of the basal current before cAMP injection from basal current after cAMP injection. (•) Current induced by cAMP injections on ACh-induced currents. (G) Statistics of the effects of isoproterenol superfusion and/or cytosolic injection of cAMP on ACh-induced current amplitude, expressed as a percentage of basal IHK. Calculated average values ± SEM are shown; the number of individual cells is given in parenthesis. (** and ***) Mean value deviates significantly ( P < 0.01 and 0.001) from the corresponding control group (i.e., oocytes not expressing heterologous β2AR in the case of Iso effects) or cAMP injection into native oocytes in the case of cAMP effects. (Left to right) Iso effect during ACh (with or without β 2AR), Iso effect upon coapplication with ACh (with or without β2AR), cAMP injection during ACh.
