Figure 8.
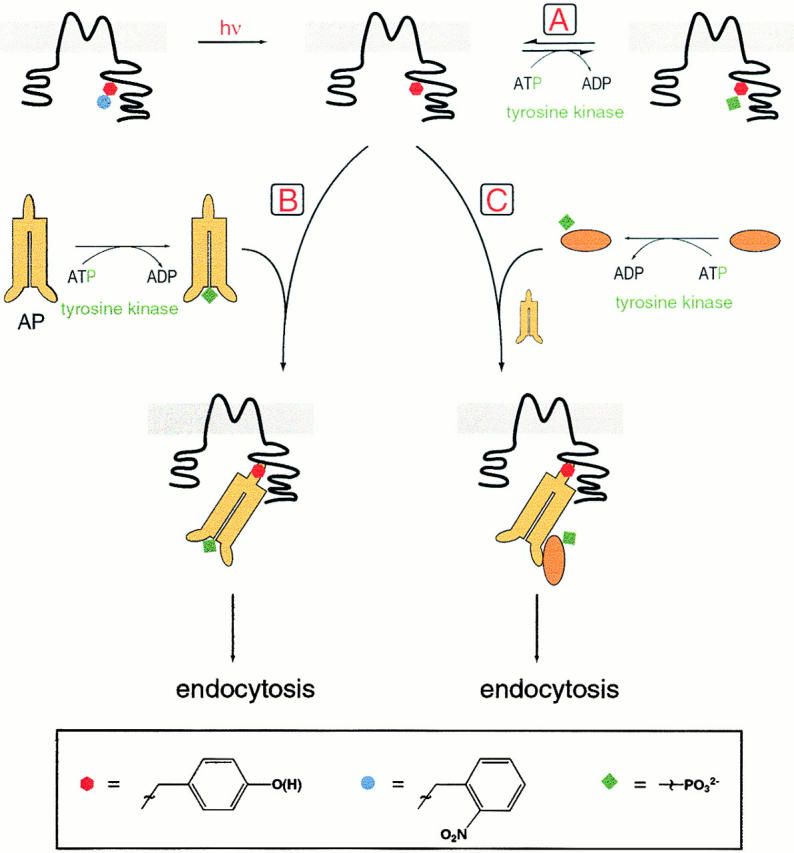
Schematic interpretation of the experiments. Irradiation leads to decaging of Tyr242 of Kir 2.1. Pathway A shows direct phosphorylation of the newly revealed tyrosine, which may be reversible/transient. Failure to observe phosphotyrosine directly makes this pathway unlikely. Pathways B and C involve the μ subunit of AP-1, AP-2, or AP-3 or a similar molecule. In pathway B the adaptor protein (AP) is phosphorylated, which enables it to bind to the now available tyrosine-based interaction motif of Kir 2.1 and inhibit the channel. Endocytosis follows. Pathway C includes phosphorylation of an unspecified protein, which, in combination with the adaptor protein, binds to and inhibits Kir 2.1 and leads to endocytosis.
