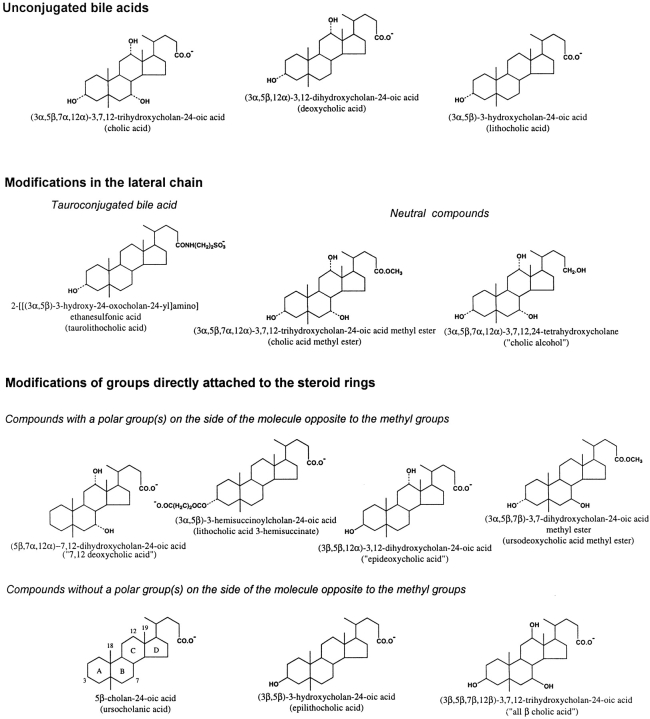
Figure 1.
Conventional chemical representation of the molecular structure of bile acids and analogues. The free carboxyl group (pKa ≅ 5) at the end of the lateral chain is shown in its ionized form, which predominates in the experimental conditions used (pH 7.4). The numbers of critical carbon atoms in the steroid nucleus (ring structure), to which chemical groups are attached, are shown in the structure of ursocholanic acid. For substitution groups, a dotted line indicates the α-configuration, whereas a continuous line indicates the β-configuration. Both chemical names and common or “created” names (the latter in parentheses) are provided.