Figure 2.
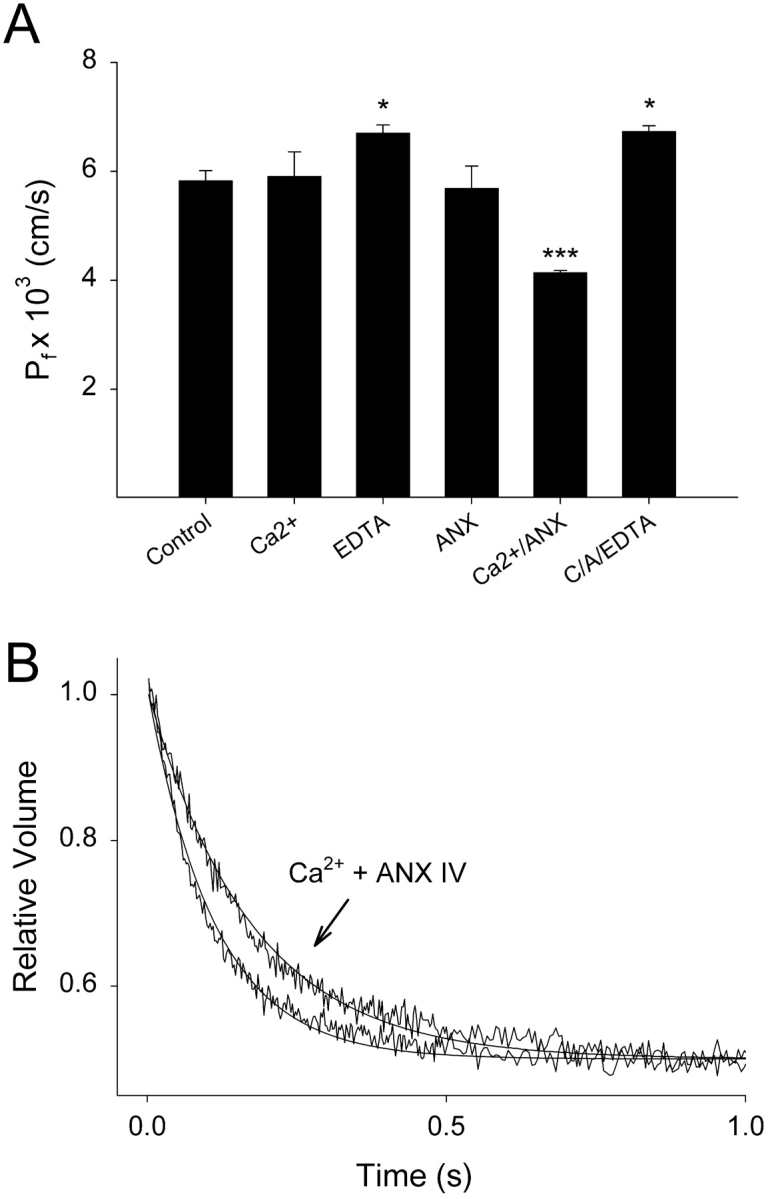
Water permeability of PC:PS liposomes is reduced upon Ca2+-induced binding of annexin A4 to membranes. Water permeability of liposomes was measured by stopped-flow fluorometry 20 min after additions were made. (A) Addition of Ca2+ or Anx4 alone did not affect the osmotic water permeability coefficient (Pf) of the liposomal membrane. Addition of EDTA alone slightly increased water permeability (P < 0.05). Addition of Ca2+ and Anx4 together for 20 min resulted in a highly significant reduction in membrane water permeability (P < 0.001), which was reversible within 2 min by the subsequent addition of 5 mM EDTA (C/A/EDTA; n = 3–6 for each condition, mean ± SEM). (B) Stopped-flow tracings showing relative rates of vesicle shrinkage following exposure of liposomes to a sudden osmotic gradient. Liposomes treated with Ca2+ and Anx4 shrink more slowly than controls. Single exponential curves have been fitted to the fluorescence data.
